- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Proteomics
Proteomics refers to the totality of all proteins present in a living organism, tissue, cell or cell compartment at a certain point in time under defined conditions. The proteome is subject to constant change, as proteins are constantly being synthesised or degraded. Proteomics analysis is therefore mainly concerned with sample preparation and the separation of proteins, enzymes, peptides and amino acids. It also includes RNA and DNA analysis in some cases.
Sample preparation primarily includes protein extraction, peptide purification and phosphopeptide enrichment.
A range of chromatographic separation methods are available for analysing proteins and peptides. These include reversed-phase chromatography, hydrophilic and hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HILIC and HIC), ion exchange chromatography (IEX), size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and affinity chromatography (AFC).
Below you will find further information and catalogue material with application examples from various manufacturers for the analysis of proteins, peptides and amino acids as well as DNA, RNA and other related substances.
Below you will find more detailed information with application examples for analysing specific proteins, peptides, DNA, RNA, antibodies, amino acids, etc.
Products
Technical Data
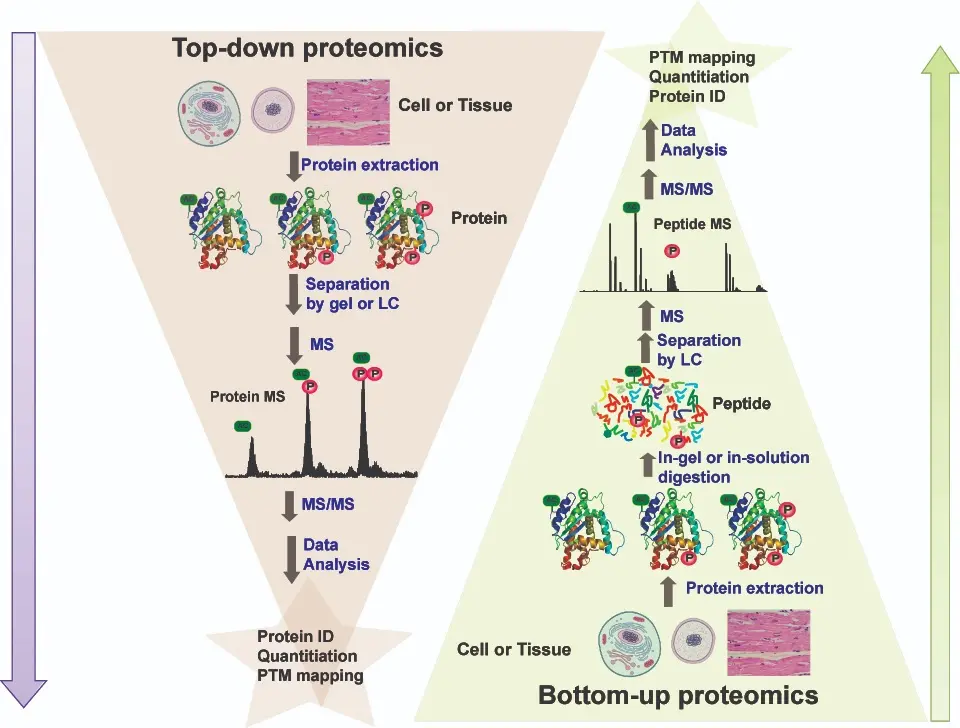
Top-Down versus Bottom-Up Approach
A large number of proteins and peptides play an important role in the analysis of proteomics. Mass spectrometry (MS) is often used to detect these analytes. There are two different approaches for the MS analysis of proteomics: top-down and bottom-up.
Top-down is used to analyse and fragment intact proteins by ESI-MS (Electron Spray Ionisation) in the gas phase. The large number of different charge variants of the proteins can lead to complicated spectra. Liquid chromatography can help to separate complex samples before they are detected by ESI-MS. The top-down approach can be used to recognise degradation products and sequence variants, which help to solve interference problems and determine post-translational modifications.
Bottom-up describes the approach in which the proteins are first enzymatically cleaved (also called digestion, often tryptic digest). The resulting peptides can then be analysed by mass spectrometry. Individual proteins or a mixture of proteins can be cleaved. This enzymatic cleavage yields thousands to hundreds of thousands of peptides, which is why a two-dimensional approach can be helpful. The original proteins can then be identified by comparison with theoretical peptide masses or a database.
Downloads
- AMT HALO Bioclass Brochure
- AMT HALO Analysis of proteins
- AMT HALO 1.5mm Column 1000Å C4 Sensitivity Increase of Mixed Proteins Application
- AMT HALO 2 MZ-Apps Peptides & Proteins ES-C18 Lot Reproducibility Application
- AMT HALO MZ-Apps Rp HALO 400Å C4 Protein Columns
- AMT HALO Fast Peptide Separation with HALO 2 Peptide ES-C18 Application
- AMT HALO 2 ES C18 Peptide High Temperature Low pH Stability Application
- AMT HALO 2 ES C18 Peptide Peak Capacity Application
- AMT HALO 2 MZ-Apps Peptides & Proteins ES-C18 Lot Reproducibility Application
- AMT-HALO® Separation of PNGase-Released & Labeled N-Glycans
- AMT-HALO® Separation of Procainamide-Labeled Dextran Standards
- AMT HALO MZ-Apps HALO-Glycan Information Sheet
GL Sciences
Sample preparation - Tryptic Digest:
- MonoTip Trypsin
Sample preparation - Desalting and enrichment:
- MonoTip C18
Sample preparation - Phosphopeptide enrichment:
- Titansphere
- Titansphere Phos-TiO Kit
- Titansphere Phos-TiO MP Kit
- Titansphere Phos-TiO for large samples
Sample preparation - Desalting of phosphopeptides:
- GL-Tip SDB
- GL-Tip GC
- MonoTip TiO
Sample preparation - removal of phosphopeptides:
- MonoSpin Phospholipid
Sample preparation - purification and enrichment of small samples:
- MonoSpin Series
Sample preparation - peptide fractionation:
- GL-Tip SCX
- GL-Tip SDB-SCX
Sample preparation - antibody purification:
- MonoSpin ProA
- MonoSpin ProG
Proteomics - Reversed Phase:
- MonoCap C18
- ProteoSil 300-C18
- ProteoSil 300-C8
- ProteoSil 200-C18
- ProteoSil 100-C18
- ProteoSil 300-C4
- MonoSelect RP-mAb
Proteomics - HILIC:
- MonoCap HILIC
- ProteoSil HILIC
Proteomics - SEC:
- ProteoSil 300-SEC
- ProteoSil 100-SEC
Proteomics - IEX:
- MonoCap SCX
Proteins and peptides - Reversed phase:
- Inertsil WP300 C18
Proteins - SEC:
- Inertsil WP300 Diol
- GL Sciences Bio General Catalogue
- GL Sciences Bioanalysis Catalogue
- GL-Sciences ProteoSil - MonoSelect Bioseparation Solution Bio LC Columns
- GL-Sciences Inertsil WP300 C18 Analysis of Peptides and Proteins Applications
- GL-Sciences Inertsil WP300 Diol Analysis of Protein Applications
- GL-Sciences ProteoSil Applications
- Imtakt Biochemicals and Metabolites Applications
- Imtakt Intrada Amino Acid 55 Amino acids Standard Applications
- Imtakt Intrada Amino Acid Amino Acids in Soy Source Applications
- Imtakt Intrada Amino Acid Amino Acids Standard (Agilent) Applications
- Imtakt Intrada Amino Acid Amino Acids Standard (Shimadzu) Applications
- Imtakt Nucleic Acids and Related Compounds Applications
- Imtakt Peptides, Proteins and Amino Acids Applications
Sepax
Proteins, peptides and antibodies - SEC:
- SRT
- Unix
- Zenix
- Nanofilm
Antibodies - IEX:
- Antibodix
Antibodies - Affinity chromatography:
- ProAqa Excel
- Affinity HSA
- Polar MC-IMAC Excel (metal affinity)
Proteomics - IEX:
- Proteomix
Proteomics - Reversed Phase:
- PolyRP
Proteomics - HIC:
- Proteomix HIC
mRNA - Affinity chromatography:
- Monomix dT20 Affinity
Adeno-associated Viruses - IEX:
- Proteomix AAV SAX
- Sepax Unix-P1002 SEC-1.8um Application Notes
- Sepax Complex Protein Sample Mixtures Analysis
- Sepax Fusion Protein Separation on SEC & SAX
- Sepax Antibodix NP10 Analysis of MAb with Charge Variance
- Sepax Antibodix NP10 Analysis of MAb-X22 Impact of Initial Salt
- Sepax Antibodix NP10 Analysis of MAb-X22 Impact of Mobile Phase Ph
- Sepax Antibodix WCX-NP3 Analysis of MAb
- Sepax Antibodix WCX-NP5 Proteomix SCX-NP5 Ion Exchange Kit for MAb-separation
- Sepax Glycomix SAX Analysis of Heparin & Heparin-like Impurities
- Sepax Glycomix SAX Zenix SEC SRT SEC-Heparin Analysis
- Sepax Mabpurix Protein-A Affinity Chromatography Resins & Columns for MAb Purification
- Sepax Nanofilm SEC SRT-C Membran Protein Separation
- Sepax Proteomix HIC-Butyl-1.7 Intact & Oxidized MAb Analysis
- Sepax Proteomix HIC-Butyl-NP5 Erbitux & Rituximab MAb Separation
- Sepax Proteomix RP-1000 Column Temperature-Effect-on-MAb Separation
- Sepax Proteomix RP-1000 Proteomix RP-500 MAb Fragment
- Sepax Proteomix SAX-NP10 Analysis of Glycoprotein
- Sepax Proteomix SAX Fast Analysis of N-Linked Sialylated Glycan
- Sepax Proteomix SAX Intact Glycoprotein Isoforms Separation
- Sepax Proteomix SCX-NP5 MAb Characterization
- Sepax Proteomix SCX-NP5 MAb-IgG1 & IgG2 Charge Variants Separation
- Sepax Proteomix SRT-SEC Zenix-C Zenix Complex Protein Sample Mixtures Analysis
- Sepax SRT-C 300 Analysis of MAb SEC
- MAb Purification on SRT-10 300
- Sepax SRT-300 Separation of Monoclonal Antibody
- Sepax Unix-C SEC-300 MAb Separation
- Sepax Unix SEC-300 1.8 Biomolecule Separation
- Sepax Zenix-C SEC-300 Rituximab Analysis
- Sepax Zenix-C SEC Analysis of Insulin and HMW Aggregates
- Sepax Zenix SEC-300 Zenix-C SEC-300 Proteomix SAX-Np5 Fusion Protein Separation
- Sepax Zenix SEC-300 Zenix-C SEC-300 SEC Screening Kit
- Sepax Zenix SEC and Proteomix Fusion Protein Separation on SEC and SAX
- sepax_sec_screening_kit
Shodex
Proteins and peptides - SEC:
- Protein KW
- Protein LW
Proteins and Peptides - Reversed Phase:
- RSpak DE
- Asahipak ODP-50
Proteins and peptides - HILIC:
- HILICpak VC-50
- Asahipak NH2P
Proteins and peptides - IEX:
- IEC QA-825
- IEC DEAE-825
- IEC SP-825
- IEC SP-FT 4A
- IEC CM-825
- IEC ES-502C 7C
Proteins and peptides - mixed mode:
- Asahipak GS-220 HQ
- Asahipak GS-320 HQ
Amino acids - IEX:
- RSpak NN-814
- IC YS-50
- CXpak P-421
Amino acids - Reversed phase:
- Asahipak ODP-50
Amino acids - HILIC:
- HILICpak VC-50
- HILICpak VG-50
- Asahipak NH2P
Nucleotides - Mixed-Mode:
- Asahipak GS-320 HQ
- RSpak NN-814
Nucleotide - Reversed Phase:
- RSpak DE
Oligonucleotides - HILIC:
- HILICpak VN-50
DNA/RNA - IEX:
- IEC DEAE-825
DNA/RNA - SEC:
- OHpak SB
- OHpak LB
- Asahipak GF-510 HQ
- Asahipak GF-M0 HQ
- Shodex HPLC Columns Catalog 2023-2024
- Shodex Asahipak C8P-50 4D High Molecular Weight Peptides Applications
- Shodex OHpak LB-806M Absolute Molecular Weight Determination of Heparin Applications
- Shodex OHpak SB-804 HQ Heparin Applications
- Shodex OHpak SB-806M HQ Heparin Applications
- Shodex PROTEIN KW-802.5 Analysis of Insulin Human According to JP Method Applications
- Shodex PROTEIN KW-802.5 Analysis of Insulin According to USP Method Applications
- Shodex PROTEIN LW-803 Comparison if SEC Separation of mAb Applications
Thermo
Peptides - Reversed Phase:
- Accucore 150-C18
Proteins - Reversed Phase:
- Accucore 150-C4
- ProSwift RP
- PepSwift
Proteins - HIC:
- MAbPAC HIC Series
- ProPac HIC
Proteins - Charge variants with IEX:
- ProPac Elite WCX
- ProPac SAX-1
- MAbPac SCX
- ProPac 3R IEX
Antibodies - affinity chromatography:
- MAbPAC Protein A
Antibodies - SEC:
- MAbPac SEC-1
- Acclaim SEC-300
- Acclaim SEC-1000
Antibody - Reversed Phase:
- MAbPac RP (Top-Down)
- BioBasic C4
Antibodies - IEX:
- ProPac Elite WCX
Glycans - HILIC:
- Accucore 150-Amide-HILIC
Glycans - Mixed-Mode:
- GlycanPac AXH-1
- GlycanPac AXR-1
Peptide Mapping - Reversed Phase:
- Hypersil GOLD VANQUISH C18
- Hypersil GOLD Peptide
- PepMap (Bottom-Up)
- µPAC (Bottom-Up)
Nucleic acids and oligonucleotides - reversed phase:
- DNAPac RP
Oligonucleotides - IEX:
- DNAPac PA200
- DNASwift SAX-1S
- DNAPac RP
Proteins and peptides - metal affinity:
- ProPac IMAC-10
Sample preparation - Digestion:
- SMART Digest
Proteins - IC:
- Dionex CarboPac PA20
- Dionex IonPac AS11-HC
- Thermo Accucore HPLC Columns for Biomolecule Separations HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo BioLC Columns Consumables HPLC Life Science Brochure 2022-23
- Thermo CX-1 LC Gradient Buffers HPLC Brochure
- Thermo Dnapac Superior Oligonucleotide Analysis HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo Glycanpac AXH-1 HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo Glycanpac AXR-1 HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo Hypersil GOLD Peptide Brochure
- Thermo Low Flow Columns Accessories HPLC UHPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo MAbPac HIC HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo MAbPac Protein A HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo MAbPac RP HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo MAbPac SCX 10 HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo MAbPac SEC 1 SEC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo PepSwift ProSwift HPLC Brochure
- Thermo ProPac 3R Brochure
- Thermo ProPac IMAC 10 HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo ProPac Elite WCX HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo ProPac HIC 10 HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo ProSwift RP HPLC Life Science Brochure
- Thermo Smart Digest Protein Digestion Life Science Brochure
- Separation of Peptides Using a Core Enhanced Technology Accucore HPLC Column
- Thermo BioBasic Characterization of mAb and ADCs Application
- Thermo Dionex Carbopac PA20 Organic Impurities in Heparin by HPAE-PAD HPLC Life Science Applications
- Thermo Dionex IonPac AS11 HC Determining of OSCS in Heparin HPLC Life Science Applications
- Thermo DNAPac RP LC-HRMS mRNA Direct Sequence Mapping HPLC Life Science Applications
- Thermo Hypersil GOLD Peptide for Reliable Monitoring of Glycopeptide Variants in mAb
- Thermo Hypersil GOLD Peptide Performance Comparison of RP C18 Columns for Peptide Mapping
- Protein A Affinity Column for Monoclonal Antibody (MAb) Titer Analysis
- Thermo MAbPac SCX Application of Salt and pH Based Ion Exchange Chromatography Gradients HPLC Life Science Applications
- Thermo Propac 3R SAX Salt Gradient AAV Analysis Application
- Thermo Propac 3R SAX Salt Gradient Protein G Analysis Application
- Thermo ProPac 3R SCX pH Gradient mAb Analysis Application
- Thermo ProPac 3R SCX Salt Gradient mAb Analysis Application
- Thermo Propac Elite WCX pH Gradient Analysis of IgG1 HPLC Life Science Applications
- Thermo Propac Elite WCX Therapeutic Protein Analysis HPLC Life Science Applications
- Thermo Bottom-Up Proteomic Profiling with µPAC HPLC Columns
- Thermo High Throughput, Routine and Comprehensive Proteome Analysis using µPAC HPLC Columns
- Thermo Oligonucleotide Characterization using µPAC Columns
- Thermo Peptide Separation on µPAC HPLC Columns
- Thermo Routine Proteome Analysis using 50 cm µPAC Columns
Tosoh
Proteins and peptides - SEC:
- TSKgel SW
- TSKgel SWXL
- TSKgel SuperSW
- TSKgel UltraSW
- TSKgel UP-SW
Amino acids - IEX:
- TSKgel SAX
- TSKgel SCX
Peptides and small proteins - IEX:
- TSKgel Q-STAT
- TSKgel SP-STAT
- TSKgel CM-STAT
- TSKgel SCX
- TSKgel SP-2SW
- TSKgel CM-2SW
- TSKgel DEAE-2SW
Peptides - HIC:
- TSKgel Butyl-NPR
Proteins - IEX:
- TSKgel BioAssist S
- TSKgel BioAssist Q
- TSKgel Q-STAT
- TSKgel SP-5PW
- TSKgel DEAE-5PW
- TSKgel CM-5PW
- TSKgel SP-STAT
- TSKgel CM-STAT
- TSKgel SP-NPR
- TSKgel DEAE-NPR
- TSKgel SuperQ-5PW
Proteins - HIC:
- TSKgel Phenyl-5PW
- TSKgel Ether-5PW
- TSKgel Butyl-NPR
Proteins - Reversed Phase:
- TSKgel Protein C4-300
- TSKgel TMS-250
Nucleosides - IEX:
- TSKgel SP-2SW
- TSKgel DEAE-2SW
Nucleotides - IEX:
- TSKgel Q-/DNA-STAT
- TSKgel DEAE-2SW
Peptides, oligonucleotides, nucleobases - HILIC:
- TSKgel Amide-80
Oligonucleotides - IEX:
- TSKgel Q-/DNA-STAT
- TSKgel DEAE-5PW
- TSKgel DEAE-NPR
- TSKgel DNA-NPR
- TSKgel SuperQ-5PW
Oligonucleotides and DNA/RNA - HIC:
- TSKgel Phenyl-5PW
- TSKgel Butyl-NPR
Oligonucleotides and DNA/RNA - Reversed Phase:
- TSKgel Oligo-DNA RP
DNA/RNA - IEX:
- TSKgel Q-/DNA STAT
- TSKgel DNA-NPR
- TSKgel DEAE-NPR
- TSKgel DEAE-5PW
- TSKgel DEAE-3SW
Antibody affinity chromatography:
- TSKgel FcR-IIIA-NPR
- TSKgel Protein A-5PW
- Tosoh Chromatography Catalogue 2019
- Tosoh Assessing the Heterogeneity of the Fc-Glycan of a Therapeutic Antibody Using an engineered FcγReceptor IIIa-Immobilized Column Applications
- Tosoh SkillPak Development and scale-up of an antibody platform
- Tosoh TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A HC-650F Improve Performance of the Protein A Capturing Step Applications
- Tosoh TOYOPEARL AR-rProtein A HC-650F Protein A chromatography - The process economics driver in mab manufacturing Applications
- Tosoh TOYOPEARL AR-rProtein A Increased productivity for downstream processin of biotherapeutics Applications
- TOSOH Comparison of Toyopearl AF-rProtein a HC-650F binding capacity at various bed heights and constant linear velocity
- Tosoh TSKgel Amide-80 Glycosilation Analysis Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Amide-80 N-Glyco Mapping of the ZP-domain of Murine TGFR-3 Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Amide-80 Separation of Peptides by HILIC Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Butyl-NPR TSKgel G3000SWXL mAb Aggregate Detection Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel DEAE-5PW Separation of Membrane Protein by IEX Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Ether-5PW Separation of Membrane Protein by HIC Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel FcR-IIIA-NPR Characterization by Top Down MS Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel G2000SWXL Separation of Low Molecular Mass Heparin by SEC Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel G3000SWXL Analysis of mAb and Proteins Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel G3000SWXL SEC-UV-RI-MALS Analysis of Protein Aggregates Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel G3000SWXL TSKgel SuperSW mAb HR TSKgel SuperSW mAb HTP High Speed and Resolution SEC Analysis of mAbs Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel G3000SW Separation of Membrane Protein by SEC Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Octadecyl-NPR TSKgel Octadecyl-4PW Separation of Standard Proteins by RPC Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Protein A-5PW Fast mAb Titer Determination Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Protein A-5PW Reproducible and Robust Antibody Titer Analysis Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Protein C4-300 RP Analysis of Antibody Fragments Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel SP-STAT TSKgel CM-STAT Fast Analysis of IgG Charge Heterogeneity Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel SuperSW mAb HR Separation of mAb Monomer from its Half-body Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel SuperSW2000 Separation of Mixture of Proteins and Peptides Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel UP-SW3000-LS SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel UP-SW3000 UHPLC Analysis of Immunoglobulins Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel UP-SW3000 Inceased Monoclonal Antibody Resolution Applications
Waters
Peptides - UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Acquity UPLC Peptide CSH C18, 1.7µm
- Acquity Premier Peptide CSH C18, 1.7µm
- Acquity UPLC Peptide HSS T3, 1.8µm
- Acquity Premier Peptide HSS T3, 1.8µm
- Acquity UPLC Peptide BEH C18, 1.7µm
- Acquity Premier Peptide BEH C18, 1.7µm
- XSelect Peptide CSH C18, 2.5µm
- XSelect Premier Peptide CSH C18, 2.5µm
- XSelect Peptide HSS T3, 2.5µm
- XSelect Premier Peptide HSS T3, 2.5µm
- nanoEase MZ Peptide BEH C18, 1.7µm
- XBridge Premier Peptide BEH C18, 2.5µm
Peptides - Reversed Phase:
- XBridge Peptide BEH C18, 3.5µm
- BioSuite C18
- Delata-Pak
Peptides/Proteins - IEX:
- Protein-Pak HR Q
- Protein-Pak HR DEAE
- Protein-Pak HR SP
- Protein-Pak HR CM
- BioSuite SP
- BioSuite CM
- BioSuite Q
- BioSuite DEAE
Proteins - Reversed Phase:
- BioResolve RP mAb Polyphenyl, 2.7µm
- BioSuite Phenyl, 10µm
- DeltaPak C4
- Symmetry C4 300, 3.5µm, 5µm
- XBridge Protein BEH C4
Proteins - UHPLC - HILIC:
- ACQUITY Glycoprotein BEH Amide, 1.7µm
Proteins - UHPLC - HIC:
- Protein-Pak Hi Res HIC, 2.5µm
Proteins - HIC:
- Protein-Pak Hi Phenyl, 10µm
Proteins - UHPLC - IEX:
- BioSuite Anion-Exchange, 2.5µm
Proteins - UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- ACQUITY Protein BEH C4, 1.7µm
- nanoEase MZ Protein BEH C4, 1.7µm
Proteins - UHPLC - SEC:
- ACQUITY Premier Protein SEC
- BioResolve SEC mAb, 2.5µm
- XBridge Premier Protein SEC, 2.5µm
Proteins - SEC:
- BioSuite Diol (OH), 5µm
- Protein-Pak SEC
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.
















