- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
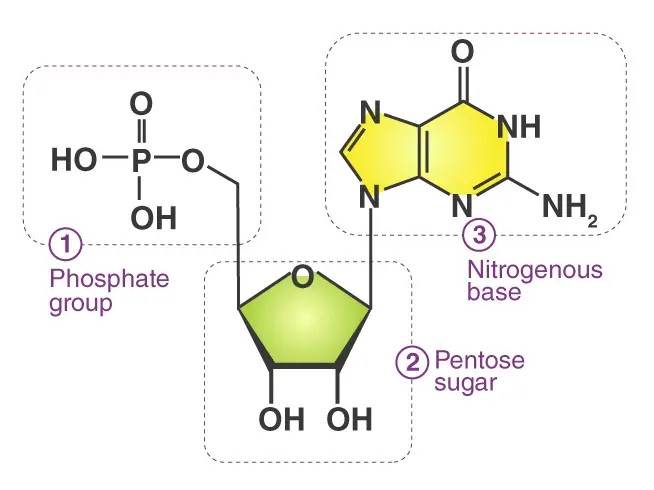
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA and consist of a base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil), a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and a phosphate group. They play a central role in many biological processes, including energy storage (e.g. ATP) and signalling.
Analysing nucleotides using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a common method for separating, identifying and quantifying these molecules. Various HPLC techniques are used, such as anion-exchange or reversed-phase HPLC, which separate nucleotides based on their charge, polarity and hydrophobic properties. HPLC enables precise and efficient analysis of nucleotide mixtures, which is of great importance in biochemistry, molecular biology and diagnostics.
Products
Technical Data
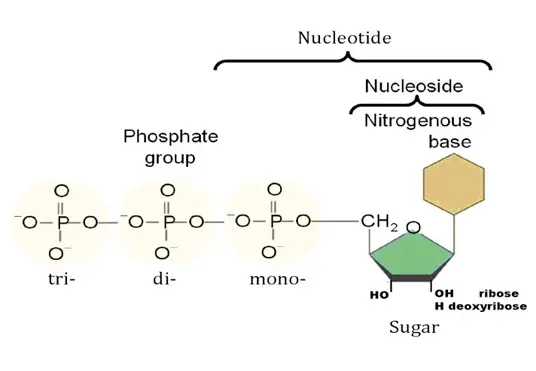
Difference between Nucleotides, Nucleosides and Nucleobases
The difference between nucleotides, nucleosides and nucleobases lies in their chemical structure:
- Nucleotides: They consist of three components - a nucleobase (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil), a sugar (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA) and one or more phosphate groups. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA and also play a role in energy metabolism (e.g. ATP).
- Nucleosides: Nucleosides consist of a nucleobase and a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), but without the phosphate group. They are therefore a precursor of nucleotides and are formed by the absence of the phosphate group.
- Nucleobases: Nucleobases are the nitrogenous bases contained in nucleotides and nucleosides. There are five main bases: Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine (only in DNA) and uracil (only in RNA).
Nucleotides = nucleobase + sugar + phosphate
Nucleosides = nucleobase + sugar
Nucleobases = the pure bases.
Difference between Nucleotides, Oligonucleotides and DNA/RNA
The differences between nucleotides, oligonucleotides and DNA/RNA lie in their structure and function:
- Nucleotides: Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. They consist of a nucleobase (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil), a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and a phosphate group. They serve as building blocks for larger molecules such as DNA and RNA and also play an important role in other biological processes such as energy transfer (ATP).
- Oligonucleotides: Oligonucleotides are short chains of nucleotides, typically between 2 and 20 nucleotides long. They are often used in research as probes, primers or for genetic engineering applications, as they contain specific sequences that can bind to DNA or RNA segments.
- DNA/RNA: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are long polymers of nucleotides. DNA consists of deoxyribonucleotides and stores genetic information, while RNA consists of ribonucleotides and is involved in protein synthesis and gene regulation in various forms. DNA is usually double-stranded, while RNA is usually single-stranded.
Applications
HILIC separation of adenosine phosphates with AMT HALO Penta-HILIC
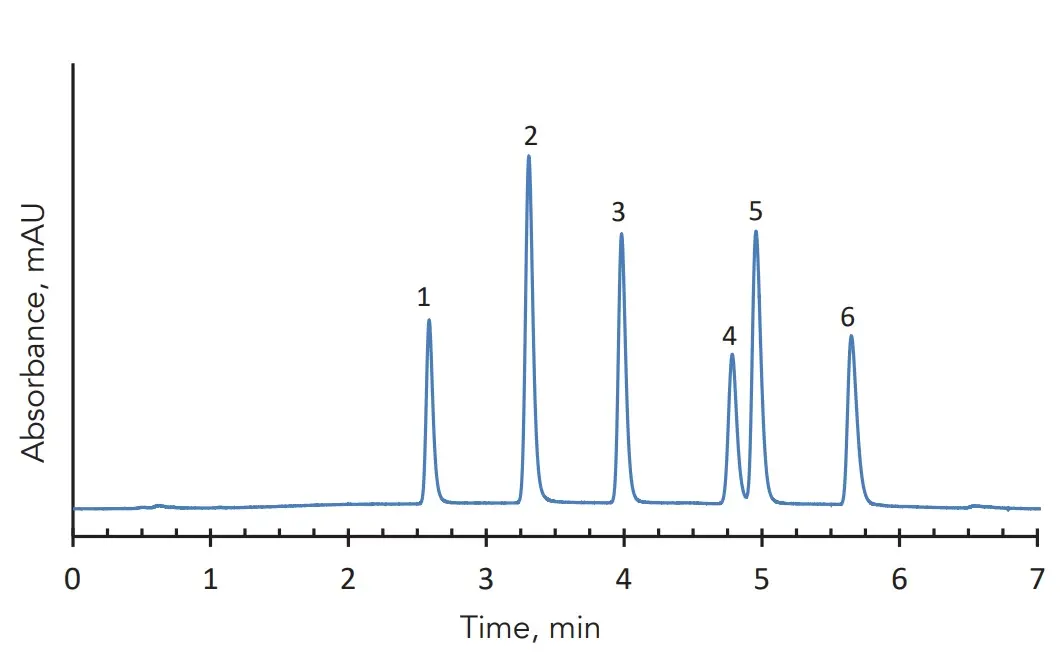
Peak identities
1. adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
2. guanosine monophosphate (GMP)
3. adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
4. guanosine diphosphate (GDP)
5. adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
6. guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
Test conditions
Column: HALO Penta-HILIC 100x2.1mm, 2.7µm (92812-605)
Mobile phase A: 50/50 acetonitrile/0.025M ammonium phosphate (pH 6)
Mobile phase B: 75/25 acetonitrile/0.025M ammonium phosphate (pH 6)
Gradient:
Time / min | %B |
0 | 90 |
8 | 40 |
Flow rate: 0.3 mL/min
Back pressure: 76 bar
Temperature: 50 °C
Detection: UV, 260 nm
Injection volume: 1 µL
Sample solvent: Mobile phase B

Reversed phase analysis of nucleotides with GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-3V
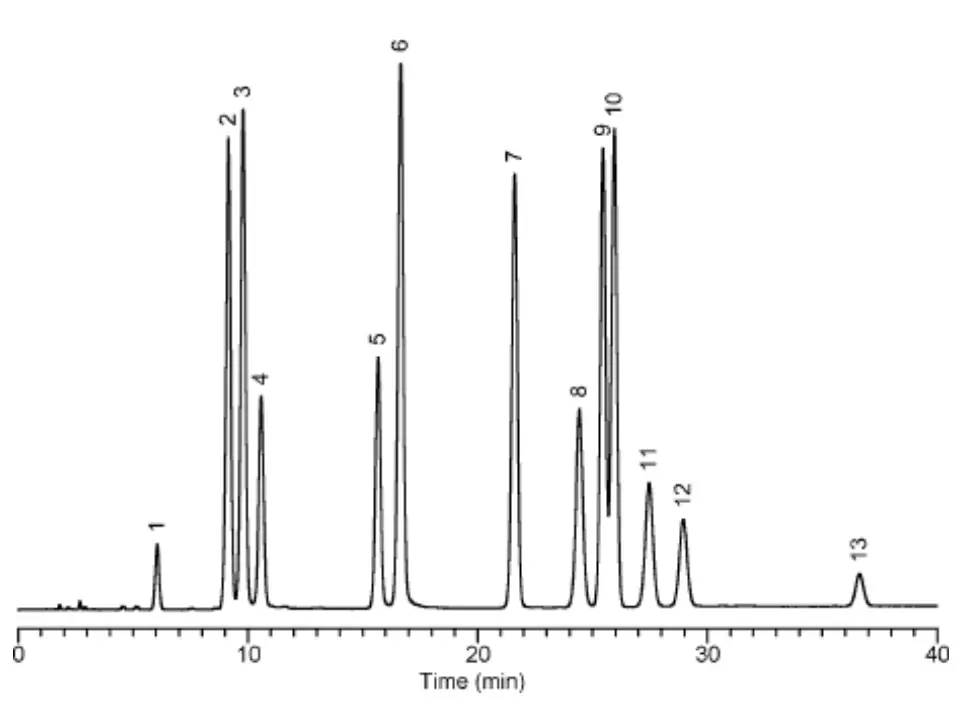
Peak identities
1. unknown 2. 5-AMP 3. 5-GMP 4. 5-IMP 5. 5-TMP 6. 3-AMP 7. 2-AMP 8. 5-ADP 9. 3.5-cAMP 10. 3.5-cGMP 11. 5-GDP 12. 5-IDP 13. 5-TDP
Test conditions
Column: Inertsil ODS-3V 150x4.6mm, 5µm
Mobile phase A: 5mM tetrabutylammonium bromide + 20mM KH2PO4 (pH 3.5)
Mobile phase B: 5mM tetrabutylammonium bromide + 20mM KH2PO4 (pH 3.5)/acetonitrile 40/60
Gradient:
Time / min | %A | %B |
0 | 95 | 5 |
5 | 95 | 5 |
35 | 76 | 24 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Temperature: 40 °C
Detection: 40 °C
Injection volume: 5 µL

Downloads
AMT
HPLC - HILIC:
- HALO Penta-HILIC, 2.7µm
ChromaNik
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Sunniest RP-AQUA, 3µm
- SunShell RP-AQUA, 2.6µm
- GL Sciences Inertsil AX Analysis of 5 Nucleotides
- Gl Sciences Inertsil NH2 Analysis of Nucleotides
- GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-2 Nucleotides
- GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-2 Nucleotides Capillary Column
- GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-3V Analysis of Bases of Nucleic and Nucleotides
- GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-3V Analysis of Nucleotides
- GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-4 Analysis of Nucleotides
- GL Sciences InertSustain Amide Analysis of Nucleotides and Nucleosides
- GL Sciences InertSustain AX-C18 Analysis of Nucleotides and Cyclic Nucleotides
- GL Sciences InertSustain C30 Analysis of ATP related Compounds and Cyclic Nucleotides
- GL Sciences InertSustain NH2 Analysis of Nucleotides
Hamilton
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- PRP-1, 5µm
- Helix Amaze HA Analysis of Adenosine Diphosphate and Adenosine Triphosphate
- Helix Amaze HD Analysis of Adenosine and Adenine
- Helix Amaze HD Analysis of Nucleosides and Nucleoside Derivatives
- Helix Amaze TCH Separation of Nucleobases and Nucleosides
- Helix Coresep 100 Ultra-fast Separation of Nucleobases
- Helix Coresep SB Separation of Nine Nucleotides
- Imtakt Intrada Organic Acid Cyclic Mononucleotides
- Imtakt Union UK-Amino Mononucleotides
- Imtakt Unison UK-Amino Adenosine Phosphates
- Imtakt Decapo DX-C18 Nucleosides and bases
- Imtakt Unison UK-Amino Nucleosides and bases
- Imtakt Intrada Organic Acid Nucleoside Triphosphates
- Imtakt Intrada Organic Acid Nucleoside Triphosphates
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleodur HILIC Separation of Adenosine
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleodur HILIC Guanosine Phosphates
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleodur PolarTec Nucleotides
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleogel SAX Nucleotides
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleoshell HILIC Nucleotides
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleoshell HILIC Separation of eight Nucleotides
- Macherey-Nagel Nucleosil C18 Detection of Nucleotides and Related Compounds
Osaka Soda
HPLC - IEX:
- Capcell PAK NH2, 5µm
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Capcell PAK ADME, 5µm
- Capcell CORE AQ, 2.7µm
Sepax
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- HP-C18, 5µm
HPLC - IEX:
- Proteomix SAX, 5µm
Shimadzu
HPLC - IEX:
- Shim-pack WAX-1, 3µm
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Shim-pack GIST C18-AQ, 3µm
- Shim-pack Scepter C18, 3µm
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Shim-pack XR-ODSIII, 2.2µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- Shim-pack Mix-HILIC, 5µm
- Shimadzu Shim-pack Mix HILIC Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrophilic Metabolites
- Shimadzu Shim-pack WAX-1 Analysis of Mononucleotides
- Shimadzu Shim-pack XR-ODSIII Ultrahigh Separation Analysis of Nucleotides
- Shimadzu Shim-pack GIST C18-AQ Analysis of Nucleic Acid Related Substances
- Shimadzu Shim-pack Scepter C18 Achieving Improved Sensitivity and Reliable Analytical Performances in Nucleotides Analysis
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Adenine Nucleotides in Red Blood Cell
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Nucleobases, Nucleosides and Nucleotides
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Umami Nucleic Acids
- Shodex IEC DEAE-825 Nucleotides
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Adenosine Derivatives
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Analysis of ATP and its Related Substances in Muscle of Fish and Shellfish
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Cyclic AMP and AMP
- Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ Nucleobases
- Shodex RSpak DE-413 Nucleobases
- Shodex RSpak DE-613 Nucleobases and Nucleosides
- Shodex RSpak NN-814 Nucleobases and Nucleosides
Thermo
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Accucore aQ, 2.6µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- Accucore Amide-HILIC, 2.6µm
HPLC - IEX:
- DNAPac PA100
HPLC - Ion chromatography:
- IonPac AS11-HC, 4µm
Tosoh
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- TSKgel ODS-120T, 5µm
- Waters ACQUITY BEH Amide Atlantis Premier BEH Z-HILIC Improved Separation of RNA Nucleotides, Nucleosides and Nucleobases
- Waters ACQUITY BEH Amide Separation of Nucleotide Phosphates
- Waters ACQUITY HSS T3 Demonstrating Improved Sensitivity and Dynamic Range with MaxPeak High Performance Surfaces (HPS) Technology: A Case Study on the Detection of Nucleotides
- Waters Atlantis Premier BEH Z-HILIC Isocratic Separation of RNA Nucleotide Triphosphates Including Pseudouridine
- Waters XTerra MS C18 Nucleotide Triphosphates
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.




























