- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Size Exclusion Chromatography SEC/GPC
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC), also known as gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and gel filtration chromatography (GFC), is a chromatographic process in which analytes are separated according to size and structure. It is used to characterise natural and synthetic polymers, biopolymers, proteins and nanoparticles.
The largest molecules are the first to leave the separation column. The smaller the molecules are, the better they can penetrate the pores of the stationary phase and the later they are eluted from the column (see illustration).
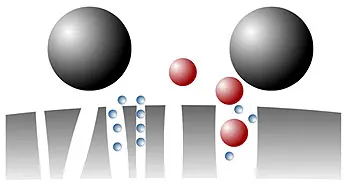
Subcategories of size exclusion chromatography
Products
Technical Data
Basics
Stationary phases of the SEC
Either porous silica or polymer-based materials are used as stationary phases. In order to minimise adsorption or other undesirable interactions between the analyte and the stationary phase, some of these are modified or undergo special treatment during the manufacturing process. Polymer materials for the GFC are usually based on polymethacrylate or polyhydroxymethacylate. Styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer (PS-DVB) is often used for polymer-based GPC columns.
Mobile phases of SEC
Aqueous mobile phases are used in gel filtration chromatography (GFC). GFC is used as a bioseparation technique for the separation of proteins and other large biomolecules. Gel permeation chromatography (GPC), on the other hand, uses organic mobile phases to separate non-polar polymers (plastics).
SEC detectors
In principle, the same detectors can be used for size exclusion chromatography as in HPLC. In addition, light scattering and viscosity detectors are also used for polymer analysis in order to obtain specific molecular and structural information about the analyte. When SEC is combined with light scattering, viscometers and concentration detectors (known as triple detection), it can calculate absolute molecular weight, molecular size and intrinsic viscosity as well as provide information on macromolecular structure, conformation, aggregation and branching.
Reference materials for SEC
By using reference materials with known molecular size and distribution, the GPC system can be calibrated to allow precise analysis of molecular weights and molecular size distribution in a sample. Calibration standards are essential to regularly check the performance of the GPC system and ensure that results are consistent and reliable over time. These standards also help to optimise separation conditions and improve analytical accuracy, making them a critical component of high quality GPC analysis. MZ-Analysentechnhik GmbH offers you a wide range of different SEC reference materials from manufacturers such as Sigma Aldrich, Tosoh, Shodex or Waters.
Columns for the SEC/GPC
To select a suitable column, a few basic questions should be clarified first.
1. What is the polarity of the analyte and which solvents are suitable?
For very polar biomolecules, such as proteins or antibodies, purely aqueous buffers are often used as eluents. Silica gel has proven to be a suitable base material for this. For polar to medium polar polymers, aqueous or polar organic eluents or mixtures of both are used. The base material is often polymethacrylate or polyvinyl alcohol. For non-polar polymers for whose analysis purely organic eluents are used, styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers (PS/DVB) are usually used as stationary phases.
2. What is the molecular weight of my analyte?
The molecular weight of the analyte or its size in the solvent determines the pore size of the stationary phase. The absolute pore sizes range from about 25 to 30,000 Å, covering a molecular weight range of about 100 to > 20,000,000 Daltons. For samples with very different molecular weights, either several columns with different pore sizes can be connected in series or columns containing particles with different pore sizes can be used. These are often labelled "linear", "mixed gel" or "multipore gel".
In many cases, suitable pore sizes can be easily determined with the help of the usually very extensive calibration data provided by the manufacturers.
1. columns for organic mobile phases (GPC)
| Manufacturer | Column lines | Characteristics |
| MZ-Analysentechnik GmbH | Base material: PS/DVB | |
| MZ-Analysentechnik GmbH | MZ-SuperFG | Base material: silica gel |
| Shodex™ | K-800 Series | Base material: PS/DVB |
| Shodex™ | KF-600 Series | Base material: PS/DVB |
| Shodex™ | LF Series | Base material: PS/DVB |
| Shodex™ | HT and UT Series | For high temperature applications up to 210 °C |
| Shodex™ | HFIP Series | For HFIP as eluent |
| Tosoh Bioscience™ | Base material: Highly cross-linked polymethacrylate | |
| Tosoh Bioscience™ | Base material: PS/DVB | |
| Sepax™ | Base material: PS/DVB | |
| Macherey-Nagel™ | Base material: PS/DVB | |
| Waters™ | Base material: PS/DVB | |
| SMT™ | Base material: silica gel |
2. columns for aqueous mobile phases (GFC) and aqueous/organic mobile phases
| Manufacturer | Column lines | Characteristics |
| Tosoh Bioscienace | Base material: silica gel | |
| Tosoh Bioscience | Base material: polymethacrylate | |
| Shodex™ | K-800 Series | Base material: Silica gel |
| Shodex™ | SB-800HQ Series | Base material: Polyhydroxymethacrylate |
| Shodex™ | LB-800 Series | Base material: Polyhydroxymethacrylate |
| Shodex™ | Base material: Polyvinyl alcohol | |
| Sepax™ | Base material: silica gel | |
| Sepax™ | Base material: silica gel | |
| Mitsubishi Chem. Corp.™ | Base material: Hydrophilic polymer | |
| Supelco | Base material: silica gel | |
| Waters™ | Base material: Polyhydroxymethacrylate |
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.
