- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Sugar
Analysis and Separation of Saccharides and Derivatives
Efficient and reliable analysis of food and its ingredients has become increasingly important in recent years, as the requirements for food safety and the recipes used have steadily increased. Carbohydrates are a major area of food ingredients. Their analysis involves the separation of oligo- and polysaccharides, sugars, sugar alcohols, their degradation products and substitutes (e.g. sugar substitutes or sweeteners). In addition to the food industry, the analysis of wood and plant ingredients is another major field of application for carbohydrate analysis.
Technical Data
The stationary phases in the analysis of saccharides
For the analysis of carbohydrates, mostly polymer-based materials which are modified on the surface with either amino or sulphonic acid groups (-SO3X). The counterion (X) of the sulphonic acid groups can be of different types, as this can influence the selectivity of the column. In the simplest case, this is a hydrogen ion (X=H+). Other counterions used are calcium (X=Ca2+), lead (X=Pb2+), potassium (X=K+) or sodium (X=Na+). Sometimes other modifications of the base material are also used for the separation of carbohydrates, e.g. ammonium, carboxyl or diol groups.
Separation mechanisms involved
Depending on the stationary and mobile phase, different separation mechanisms can come into play, with at least two of them often running in parallel during a separation:
- Ligand exchange chromatography (LEX) (see below)
- Size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
- Ion exchange chromatography (IEX)
- Ion exchange chromatography (IEC)
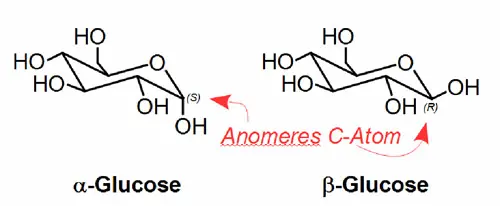
The separation of anomers
Anomers are certain diastereomers of sugar molecules that only differ in their configuration at the so-called "anomeric" carbon atom. For glucose, for example, this is α- and β-glucose (see figure). In solution, these can transform into the respective other anomer via open-chain structures. This process is known as mutarotation.
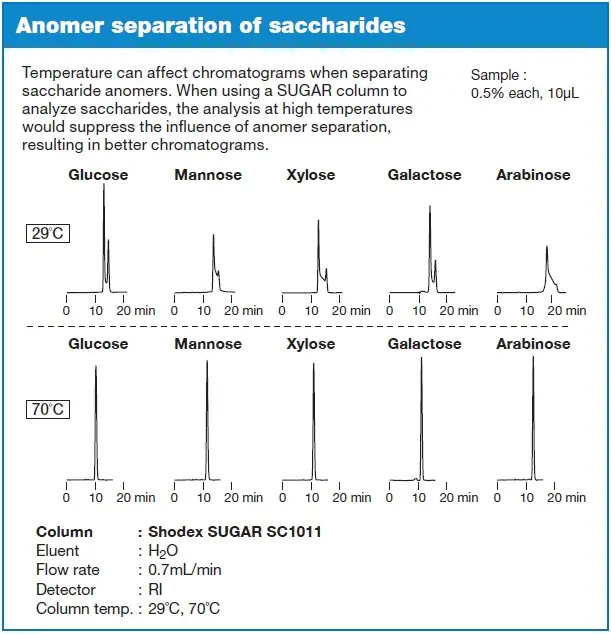
In some cases, anomers can be separated via HPLC, or broadened or split peaks result. This is often undesirable when separating different sugars and should be suppressed. There are two ways to avoid anomer separation:
- The analysis is performed at elevated temperatures (≥70 °C)
- The analysis is carried out under alkaline conditions
The analysis of sugars at elevated temperatures is usually carried out with stationary phases that have sulphonates on the surface. With amino columns, however, anomer separation may no longer be observed at room temperature, or the temperature may need to be raised to a maximum of 40 °C because the weakly basic amino groups in the stationary phase create basic conditions inside the column.
Detection possibilities when analysing saccharides
The refractive index detector (RI-detector) is often used for (routine) analyses of saccharides. This is very versatile, as the analytes do not need to have electrical conductivity or UV activity. Disadvantages compared to other detection options are the relatively low sensitivity and selectivity. The RI detector is also not suitable for gradient elution, as the refractive index also changes with the change in eluent composition.
If the analytes are UV- or fluorescence-active, a UV or fluorescence detector can be used. These have a high sensitivity and selectivity. Other detectors used for saccharide analysis are ELSD, CAD or MS detectors. These have extremely high sensitivities and selectivities and are also very versatile. The disadvantage of these detector types is their comparatively high price.
Applications
Ligand Exchange Separation of Sugars and Sugar Alcohols with Concise CarboSep CHO 87MM
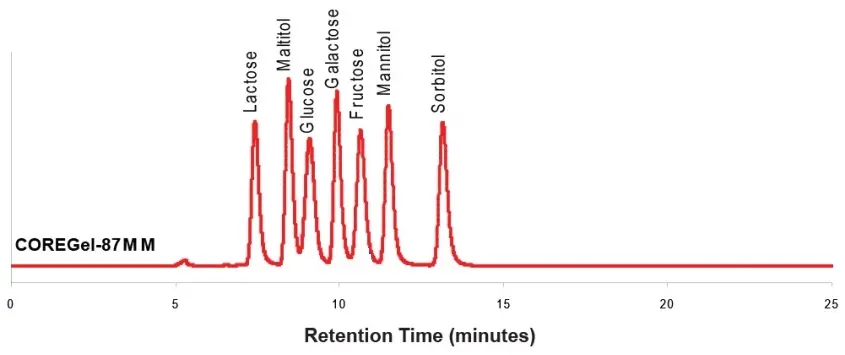
Peak identities
1. lactose 2. malitol 3. glucose 4. galactose 5. fructose 6. mannitol 7. sorbitol
Test conditions
Column: CarboSep CHO 87MM 300x7.8mm, 8µm
Mobile phase: Water
Flow rate: 0.6 mL/min
Temperature: 80 °C
Detection: RI

HILIC Separation of Sugars with Macherey-Nagel Nucleosil Carbohydrate
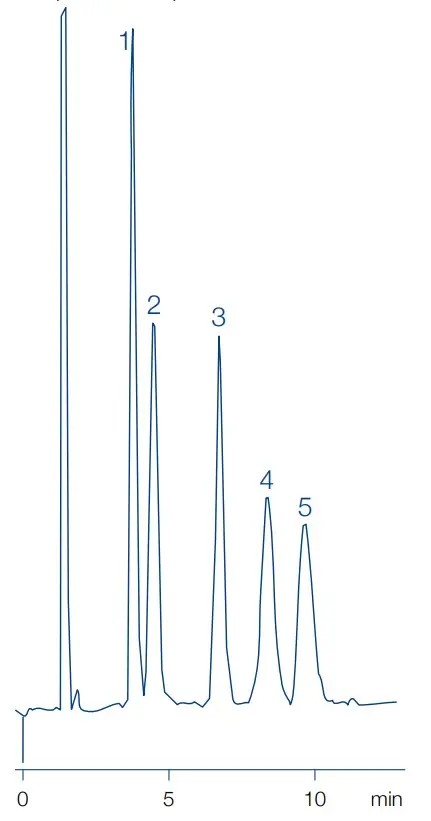
Peak identities
1. fructose 2. glucose 3. sucrose 4. maltose 5. lactose
Test conditions
Column: Nucleosil Carbohydrate 250x4.0mm, 10µm
Mobile phase: 79/21 acetonitrile/water
Flow rate: 2 mL/min
Temperature: 25 °C
Detection: RI
Injection volume: 10 µL

Downloads
Concise
HPLC - Ligand Exchange:
- CarboSep CHO 411, 20µm
- CarboSep CHO 682, 7µm
- CarboSep CHO 611, 10µm
- CarboSep CHO 611OH, 10µm
- CarboSep CHO 620, 10µm
- CarboSep CHO 782, 7µm
- CarboSep CHO 882, 7µm
- CarboSep CHO 882 FA, 7µm
- CarboSep CHO 87C FA, 8µm
- CarboSep CHO 87 MM, 8µm
- CarboSep USP L19, 8µm
- CarboSep CHO 820, 9µm
- CarboSep CHO 87C FA, 9µm
- CarboSep CHO 87C, 9µm
- CarboSep CHO 87K, 9µm
- CarboSep CHO 87N, 9µm
- CarboSep CHO 87P, 9µm
- Concise Transgenomic Carbohydrate Analysis Applications
- Concise Transgenomic CARBOSep CHO-620 CA Determination of Endogenous Glucose in Human Nerve Tissues Applications
- Concise Transgenomic CARBOSep Carbohydrate Separations Applications
- Concise Transgenomic Carbohydrate Analysis Applications
- Concise Transgenomic Carbosep CHO-87c Semi-Prep
- Concise Ttransgenomic CarboSep CHO-620
- Concise Transgenomic CarboSep CHO 682-2 Sugars and Sugar Alcohols Applications
- Concise Transgenomic CarboSep CHO-682
- Concise Transgenomic CarboSep CHO-782
- Concise Transgenomic CarboSep CHO-820
- Concise Transgenomic CoreGel-87C Galactose and Tagatose Applications
- Concise Transgenomic Coregel ORH-801 FA
Macherey-Nagel
HPLC - HILIC:
- Nucleosil Carbohydrate, 10µm
- Nucleodur 100-5 NH2-RP, 5µm
HPLC - Ligand Exchange:
- Nucleogel Sugar 810 Ca
- Nucleogel Sugar CA
- Nucleogel Sugar Pb
- Nucleogel Sugar Na
HPLC - Ion Exclusion:
- Nucleogel Sugar 810 H
- Nucleogel ION 300 OA
Merck Supelco
HPLC - Ligand Exchange:
- Supelcogel K, 9µm
- Supelcogel Pb, 9µm
- Supelcogel Ca, 9µm
- Supelcogel C-611, 9µm
- Supelcogel Ag1, 9µm
- Supelcogel Ag2, 9µm
HPLC - Ion Exclusion:
- Supelcogel H, 9µm
- Supelcogel C-610H, 9µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- Supelcosil LC-NH2, 5µm
Mitsubishi
HPLC - Ligand Exchange:
- MCI GEL CK08S, 11µm
- MCI GEL CK08E, 9µm
- MCI GEL CK08EC, 9µm
HPLC - Ligand Exchange/SEC:
- MCI GEL CK04S, 11µm
- MCI GEL CK04SS, 11µm
- MCI GEL CK02A, 20µm
- MCI GEL CK02AA, 20µm
HPLC - Ion Exclusion:
- MCI GEL CK08EH, 9µm
HPLC - IEX:
- MCI GEL CA08F, 7µm
Sepax
HPLC - Ligand Exchange:
- Carbomix Ca-NP5
- Carbomix Ca-NP10
- Carbomix Pb-NP5
- Carbomix Pb-NP10
HPLC - Ion Exclusion
- Carbomix H-NP5
- Carbomix H-NP10
Shodex
HPLC - Ligand Exchange/SEC:
- Sugar SC1011, 6µm
- Sugar SP0810, 7µm
- Sugar KS-801, 6µm
- Sugar KS-802, 6µm
- Sugar KS-803, 6µm
- Sugar KS-804, 7µm
HPLC - Ligand Exchange/HILIC:
- RSpak DC-613, 6µm
- Sugar SZ5532, 6µm
- Sugar SC1211, 6µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- Asahipak NH2P
- HILICpak VG-50, 5µm
- HILICpak VT-50, 5µm
- HILICpak VN-50, 5µm
HPLC - Ion Exclusion:
- Sugar SH1011, 6µm
- Sugar SH1821, 6µm
- RSpak KC-811, 6µm
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.
You will find:
Write us a message and we will get back to you as soon as possible.













