- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) can be a good alternative separation technique for very polar analytes that experience little retention in reversed-phase chromatography and cannot be eluted in normal-phase chromatography due to strong interactions with the stationary phase. HILIC combines the principles of normal-phase and reversed-phase chromatography by using a polar stationary phase and working with organic-rich mobile phases, which enables the analysis of highly polar molecules that are difficult to separate in traditional reversed-phase chromatography.
HILIC offers several advantages over other chromatographic methods, including improved sensitivity and selectivity for polar analytes, efficient compatibility with mass spectrometry due to the high proportion of organic solvents in the mobile phase, and the ability to analyse both polar and non-polar compounds in a single run. These features make HILIC an indispensable tool in analytical separation science, especially for complex sample matrices where polar compounds are of interest. On our site you will find information on the basics of HILIC separation technology, information on column selection as well as products from well-known manufacturers with filter function of the chemical specifications. We will be happy to assist you - just contact us!
Products
Technical Data
Basics
The HILIC separation mechanism
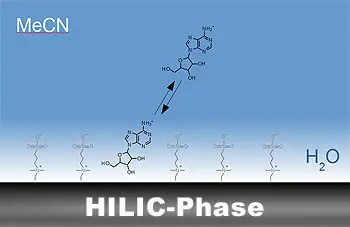
The retention mechanism is mainly based on the different distribution of the analytes between a very polar stationary phase and a less polar mobile phase. There is therefore a hydrophilic distribution equilibrium.
The water present in the eluent forms a hydrophilic layer on the surface of the stationary phase, in which polar analytes are preferentially retained and thus retarded. The water-rich layer of the stationary phase and the acetonitrile-rich mobile phase thus act as a liquid-liquid distribution system. Further influences on retention are electrostatic and van der Waals interactions as well as hydrogen bonds.
Stationary phases of hydrophilic interaction chromatography HILIC
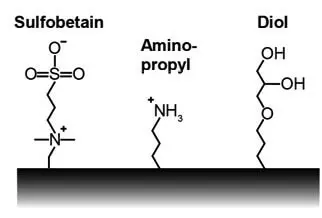
Both silica-based and polymer phases are used for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. There are neutral, singly or multiply charged phases:
1. HILIC phases with no/low ion exchange capacity
HILIC phases with no or low ion exchange capacity (IEX capacity) have neutral modifications on the surface, such as non-acidic hydroxyl, amide or urea groups. Such HILIC phases are preferably suitable for neutral or zwitterionic analytes.
2. HILIC phases with high ion exchange capacity
A. With high cation exchange capacity
HILIC phases with a high cation exchange capacity (CX capacity) have acidic groups on the surface that contain acidic hydrogen atoms, such as silanols. These show increased retention for basic analytes.
B. With high anion exchange capacity
HILIC phases with a high anion exchange capacity (AX capacity) have basic groups on the surface, such as amines. These show increased retention for acidic analytes.
| HILIC column type | Ion exchange capacity | Surface modification | Suitable for... |
| 1 | No/low IEX capacity | Neutral | Neutral/zwitterionic analytes |
| 2 | High CX capacity | Acidic | basic analytes |
| 3 | High AX capacity | Alkaline | acidic analytes |
For HILIC method development, it is advisable to use at least two, preferably three different HILIC column types.
Mobile phase of hydrophilic interaction chromatography
The mobile phase always contains a certain percentage of water or aqueous buffer. Acetonitrile is usually used as the organic component in the eluent. Water is the more strongly eluting solvent, i.e. the starting eluent (lowest elution strength) contains little water (approx. 3 to 20%). In gradient separations, the water content is slowly increased during the separation, whereby the analytes are eluted after a given time. However, isocratic separations are advantageous for HILIC separations, as the HILIC separation mechanism has slow kinetics and a longer equilibration time is required for gradient separation compared to RP columns (up to 60 times the column volume). The equilibration times depend largely on the starting conditions of the gradient. The greater the differences in the gradient composition, the longer the equilibration time.
Manufacturer of HILIC columns
A large number of manufacturers now offer columns for HILIC, which is why only a selection of columns from some manufacturers is listed below.
| Manufacturer | Name | Pore size | Modification | pH range | Surface area | HILIC column type[3] |
| ACE | HILIC N | 100 Å | Polyhydroxy | 2.0-7.0 | Neutral | 1 |
HILIC A | 100 Å | Sil | 2.0-7.0 | Acid | 2 | |
HILIC B | 100 Å | Aminopropyl | 2.0-7.0 | Basic | 3 | |
| GL Sciences | Inertsil HILIC | 100 Å | Diol | 2.0-7.5 | Neutral | 1 |
| AMT HALO® | Penta HILIC[1] | 90 Å | Pentahydroxy | 2.0-9.0 | Neutral | 1 |
HILIC[1] | 90 Å | Sil | 1.0-8.0 | Acid | 2 | |
| Kromasil | HILIC-D | 60 Å | Diol | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
| Chromanic | Sunshell HILIC amide[1] | 90 Å | Amide+hydrophilic group | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
Sunshell HILIC-S[1] | 90 Å | Sil | 1.0-5.0 | Acid | 2 | |
| Merck | SeQuant® ZIC®-HILIC | 100 Å, 200 Å | Sulfobetaine | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
SeQuant® ZIC®-cHILIC | 100 Å | Phosphorylcholine | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 | |
SeQuant® ZIC®-pHILIC | 100 Å | Sulfobetaine | 2.0-10.0 | Neutral | 1 | |
| Tosoh Bioscience | TSKgel Amide-80 | 100 Å | Carbamoyl | 2.0-7.5 | Neutral/Basic | 1/3 |
TSKgel NH2-100 | 100 Å | Amines | 2.0-7.5 | Basic | 3 | |
| Shodex | HILICpak VG-50[2] | 100 Å | Amino | 2.0-13.0 | Basic | 3 |
HILICpak VT-50[2] | 100 Å | Quaternary ammonium | 2.0-13.0 | Basic | 3 | |
Asahipak NH2P[2] | 100 Å | Amino | 2.0-13.0 | Basic | 3 | |
| Sepax | Polar-100 | 120 Å | Poly(ethylene glycol) | 1.5-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
Polar diol | 120 Å | Diol | 1.5-8.0 | Neutral | 1 | |
Polar silica | 120 Å | Sil | 1.5-8.0 | Acid | 2 | |
Polar imidazole | 120 Å | Imidazole | 1.5-8.0 | Basic | 3 | |
Polar pyridines | 120 Å | Pyridine | 1.5-8.0 | Basic | 3 | |
| Macherey nail | Nucleodur HILIC | 110 Å | Sulfobetaine | 2.0-8.5 | Neutral | 1 |
| Osaka soda | PC HILIC | 100 Å | Phosphorylcholine | 3.0-7.5 | Neutral | 1 |
| Thermo Scientific | Synchronis HILIC | 100 Å | Sulfobetaine | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
Accucore Amide-HILIC[1] | 150 Å | Polyamide | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 | |
Accucore HILIC[1] | 80 Å | Sil | 2.0-8.0 | Acid | 2 | |
Hypersil Gold Silica | 175 Å | Sil | 2.0-8.0 | Acid | 2 | |
Hypersil Gold HILIC | 175 Å | Polyethyleneimine | 2.0-8.0 | Basic | 3 | |
| Supelco | Ascentis Express OH5[1] | 90 Å | Pentahydroxy | 2.0-9.0 | Neutral | 1 |
Ascentis Express HILIC[1] | 90 Å | Sil | 2.0-8.0 | Acid | 2 | |
| Waters | BEH Amide | 130 Å, 300 Å | Amide | 2.0-11.0 | Neutral | 1 |
Cortecs HILIC | 90 Å | Sil | 1.0-5.0 | Acid | 2 | |
BEH HILIC | 130 Å | Sil | 1.0-9.0 | Acid | 2 | |
| Welch | Ultisil HILIC amide | 120 Å | Amide | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
| 120 Å | Sulfobetaine | 2.0-8.0 | Neutral | 1 |
[1] Fused-Core (Solid-Core) Particles, [2] Base Material: Polyvinylalcohol, [3] Explanation see above in "Basics of Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography"
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.