- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Acrylamide
Acrylamide is formed when food is heated to high temperatures, e.g. when frying or deep-frying. The amino acid asparagine reacts with reducing sugars such as glucose or fructose (Figure 1). Cereal products (cereals, baked goods, etc.), potato products (chips, crisps) and coffee are particularly affected.
Animal experiments have shown that acrylamide is carcinogenic and damages the genome. It has therefore been categorised as "probably carcinogenic to humans". However, there are no binding limits for acrylamide in food (in the EU). Only guide values and minimisation measures were defined in 2013 and set out in a regulation at the end of 2017. The guideline values were lowered again. This guideline value is determined by the acrylamide value, which 90% of the samples fell below. There may therefore be further lower guideline values in the future. As a result, analysing acrylamide in food has also become essential.
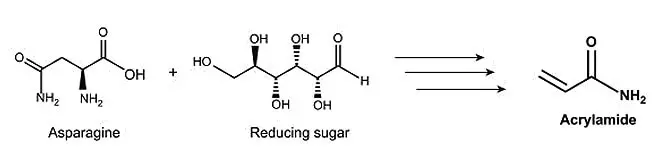
Figure 1: Formation of acrylamide.
Applications
Reversed-phase chromatography
Analysis of acrylamide, acrylonitrile and organic acids with GL Sciences Inertsil ODS-4
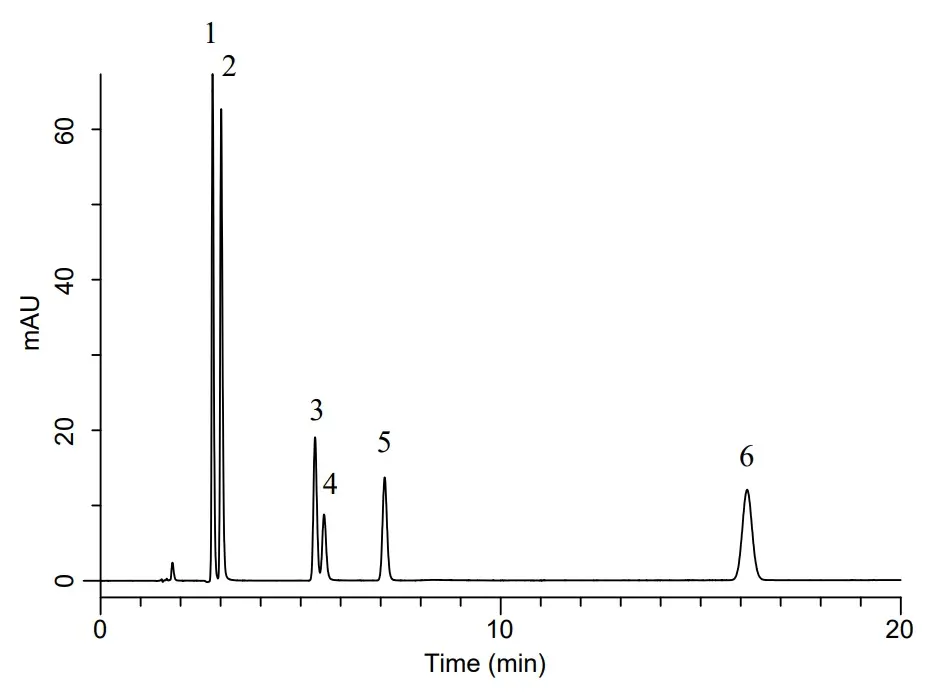
Peak identities
1. acrylamides 2. maleic acid 3. acrylic acid 4. acrylonitriles 5. itaconic acid 6. methacrylic acid
Test conditions
Column: Inertsil ODS-4 150x4.6mm, 3µm (5020-04045)
Mobile phase A: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase B: 0.1% phosphoric acid in water
Isocratic: A/B = 3/97, v/v
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Column temperature: 40 °C
Detection: UV 210 nm
Injection volume: 10 µL

HILIC
Analysis of acrylamide, methacrylamide and methyl acrylic acid with Macherey-Nagel Nucleodur HILIC
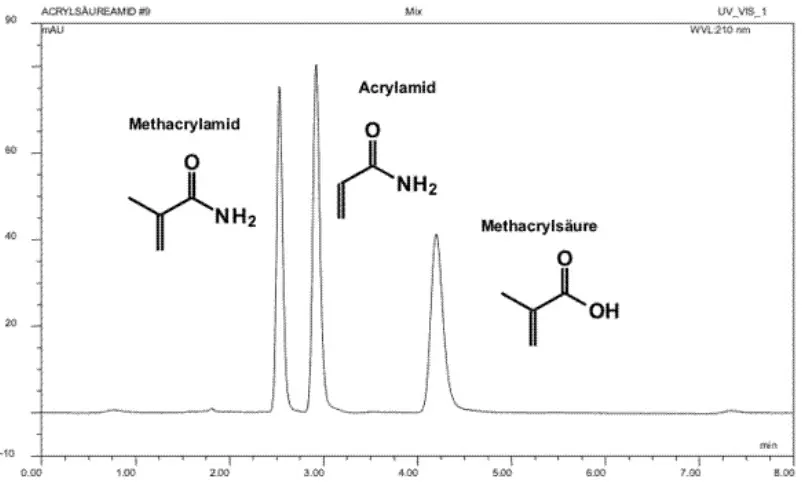
Peak identities
1. methyl acrylamides 2. acrylamides 3. methylarylic acid
Test conditions
Column: Nucleodur HILIC 125x4.0mm, 5 µm (760551.40)
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile / 0.1% formic acid (98:2, v/v)
Flow rate: 0.6 mL/min
Temperature: 22 °C
Injection volume: 0.5 µL
Detection: UV, 210 nm

Gas chromatography
Analysis of acrylonitrile, acrylamide and propionamide with GL Sciences InertCap Pure-WAX
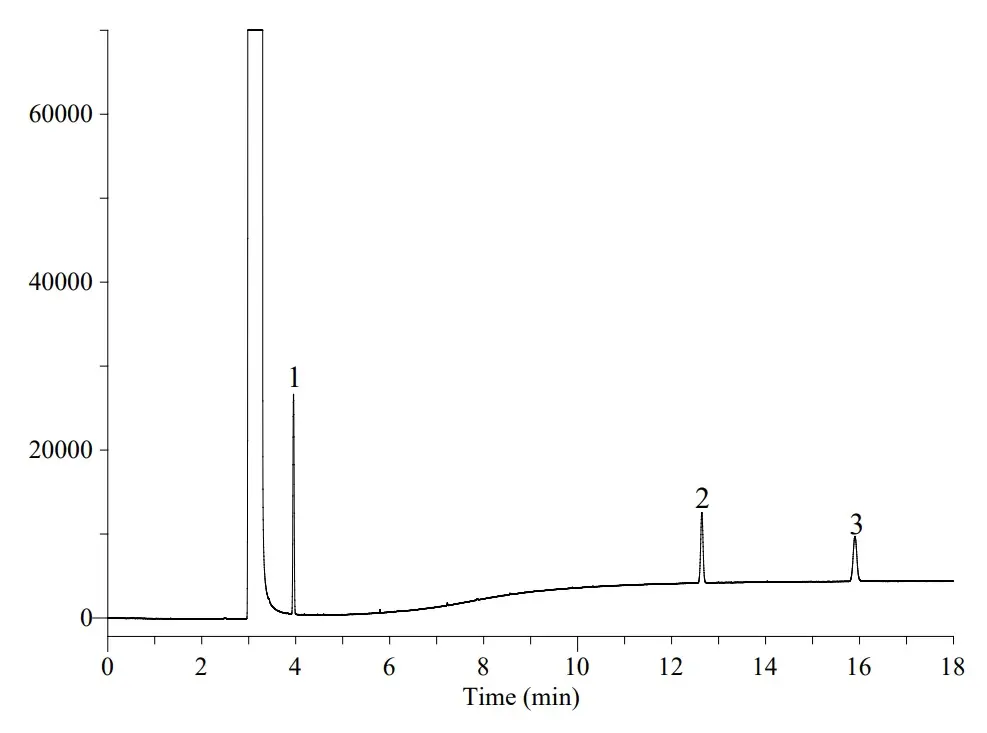
Peak identities
1. acrylonitriles 2. propionamides 3. acrylamides
Test conditions
Column: InertCap Pure-WAX 30m x 0.25mm, 0.25 µm (1010-68142)
Column temperature: 40 °C (2min hold) - 20 °C/min - 150 °C (9.5min hold)
Carrier gas: Helium 100 kPa
Injection: Split flow 50 mL/min, 200 °C
Detection: FID range 10^0, 250 °C
Sample size: 100 mg/L in methanol, 1 µL

Downloads
Based on these developments, many manufacturers have published applications for the determination of acrylamide. These range from reversed-phase chromatography, normal-phase chromatography and HILIC to gas chromatography.
Manufacturer overview
GL Sciences
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Inertsil ODS-4 3µm
GC:
- InertCap Pure-WAX
Imtakt
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Unison UK-C18
- Unison UK-C8
- Unison UK-Phenyl
- Cadenza CL-C18
HPLC - Normal Phase:
- Unison UK-Amino
- Unison UK-Silica
- Macherey-Nagel NUCLEODUR C18 Gravity Determination of Acrylamide Applications
- Macherey-Nagel NUCLEODUR C18 HTec Determination of Acrylamide in Coffee Applications
- Macherey-Nagel NUCLEOSHELL Bluebird RP 18 Separation of Organic Acid Isomers Applications
- Macherey-Nagel NUCLEODUR HILIC Separation of Acrylamide, Methacrylamide and Methacrylic Acid Applications
- Macherey-Nagel NUCLEOSHELL HILIC Separation of Acrylamide and Analogous Applications
- Macherey-Nagel NUCLEODUR HILIC Acrylamide Separation Applications
Osaka soda
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Capcell PAK C18 AQ 3µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- Capcell Cpre PC 2.7µm
Perkin-Elmer
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Altus UPLC BEH C18 1.7µm
- Restek Allure Acrylamide Acyrlamide Extracted from Potato Chips Applications
- Restek Allure Acrylamide Acrylamide Reference Standard Applications
- Restek Allure Acrylamide Comparison of 100 ppT Acrylyamide in Tap Water to a Unfortified Tap Water Applications
- Restek Stabilwax Arylamide (Potato Chip Extract) Applications
- Restek Stabilwax Acrylamide (Reference Standard) Applications
Shimadzu
GC:
- CP-Sil 24 CB
Shodex
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- RSpak DE-413 (polymer column)
Sielc
HPLC - Mixed Mode:
- Primesep 200 3µm
Merck Supelco
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Discovery HS F5 5µm
Sample preparation:
- Discovery DSC-MCAX
- Discovery DSC-C18
Thermo Fisher
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Hypercarb 5µm
HPLC - Ion chromatography:
- Dionex IonPac ICE-AS1 7.5µm
Gas chromatography:
- TarceGOLD TG-WaxMS
Sample preparation:
- HyperSep SLE96-well plate
- HyperSep Hypercarb SPE
- Thermo Hypercarb MS Assay for the Determination of Acrylamide From Foodstuffs HPLC Applications
- Thermo Dionex IonPac ICE AS1 Fast Determination of Acrylamide in Food Samples HPLC Applications
- Thermo TraceGOLD Tg WAX MS Determination of Acrylamide in Food Products and Coffee GC Applications
- Thermo TraceGOLD Tg WAX MS Acrylamine in Potato Chips GC SPE Applications
Tosoh
HPLC _ Reversed Phase:
- TSkgel ODS-100V 5µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- TSKgel Amide-80 5µm
Waters
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Atlantis dC18 5µm
- Atlantis dC18 3µm
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- ACQUITY HSS C18 SB 1.8µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- XBridge Amide 3.5µm
UHPLC - HILIC:
- ACQUITY BEH Amide 1.7µm
Sample preparation
- Oasis HLB SPE
- Oasis MCX SPE
- Waters Atlantis DC18 Acrylamide-in-Potato-Chips HPLC Applications
- Waters Atlantis DC18 Determination-of-Acrylamide HPLC Applications
- Determination of Acrylamide in Processed Foods using ACQUITY I-Class and Xevo TQ-S micro : Waters
- Waters Acquity UPLC-HSS-C18-SB Determination-of-Haloacetic-Acids & Acrylamide-in-Drinking-Water
- Waters Acquity UPLC BEH Amide Analysis-of-Acrylamide Methacrylic Acid & Methacrylamide Applications
- Waters XBridge Amide Applications Notebook
Which
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Ultisil XB-C18 3µm
Sample preparation:
- Welchrom C18E
ZirChrome
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- ZirChrom-CARB
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.
You will find:
Write us a message and we will get back to you as soon as possible.





























