- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Preservatives and Sweeteners
Preservatives are chemical substances that prevent the growth of moulds, yeasts and bacteria in foods and therefore help to extend their shelf life. Examples include benzoic acid and its salts, various sulphites, nitrites and nitrates.
Sweeteners are used as substitutes for sugar. Their sweetening power is often many times higher than that of ordinary household sugar (sucrose). Sweeteners are sometimes used in combination with each other to optimise the sweetening power on the one hand and to minimise the negative taste characteristics that sometimes occur on the other. Most sweeteners have a very low or almost no physiological calorific value.
Like household sugar, sugar substitutes are carbohydrates and are also used as sugar substitutes, although they have a lower impact on blood sugar levels than sucrose. Examples include various sugar alcohols such as sorbitol or xylitol. For the analysis of sugar alcohols, see sugar analysis.
Typical preservatives and sweeteners are often analysed using reversed-phase HPLC (RP-HPLC). Some examples are shown below.
Products
Technical Data
1. Synthetic Sweeteners with the Structural Unit of a Sulphamic Acid in the Molecule:
Acesulfame-K (E950) is a heterocyclic compound that is used as a potassium salt. Its sweetening power is about 200 times that of sucrose.
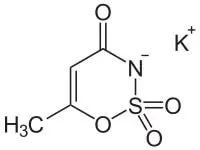
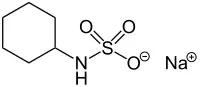
Sodium cyclamate (E952) is the sodium salt of cyclohexylsulphamic acid. The sweetening power is about 35 times that of sucrose.
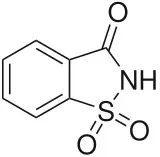
Saccharin (E954) is a heterocyclic compound derived from phthalimide. Saccharin is also often used as a salt (Na, Ca or K salt). Its sweetening power is about 500 times that of sucrose.
2. Synthetic Sweeteners with a Basic Peptide Structure
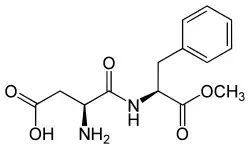
Aspartame (E951) is a dipeptide consisting of L-aspartic acid and L-phenylalanine, whose C-terminus (on phenylalanine) is present as a methyl ester (H-Asp-Phe-OMe). The sweetening power is about 200 times that of sucrose.
Neotame (E961) is made up of the compounds aspartame and 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde, which are formally linked via reductive amination. The sweetening power is about 10,000 times that of sucrose.
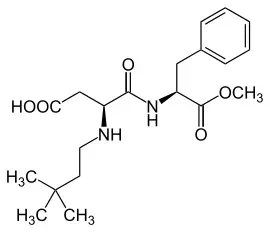
Advantam (E969) is an extremely strong sweetener, but is only used comparatively rarely. Like neotame, advantame is a modified aspartame and has a sweetening power that is up to 37,000 times higher than that of sucrose.
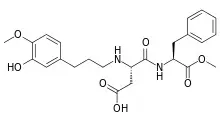
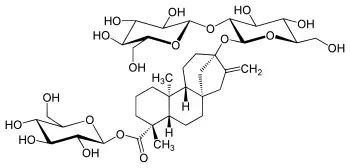
3. Steviol Glycosides (Stevia)
Stevia (E960) is a mixture of substances that is obtained from the Stevia rebaudiana plant in a multi-stage purification and extraction process. It contains a very high proportion of various steviol glycosides, e.g. stevioside or rebaudioside A. The central structural unit of the steviol glycosides is the diterpene steviol. The sweetening power of the extract is at least 200 times that of sucrose.
4. Thaumatin - a Protein-based Sweetener
Thaumatin is a protein consisting of 207 amino acids and a molecular mass of around 22 kDa. The protein, which can be used as a sweetener, is found in the West African catemafruit. Its sweetening power is about 2000 times that of sucrose.
Applications
Reversed Phase Analysis of Preservatives and Sweeteners with GL Sciences Inertsil Ph
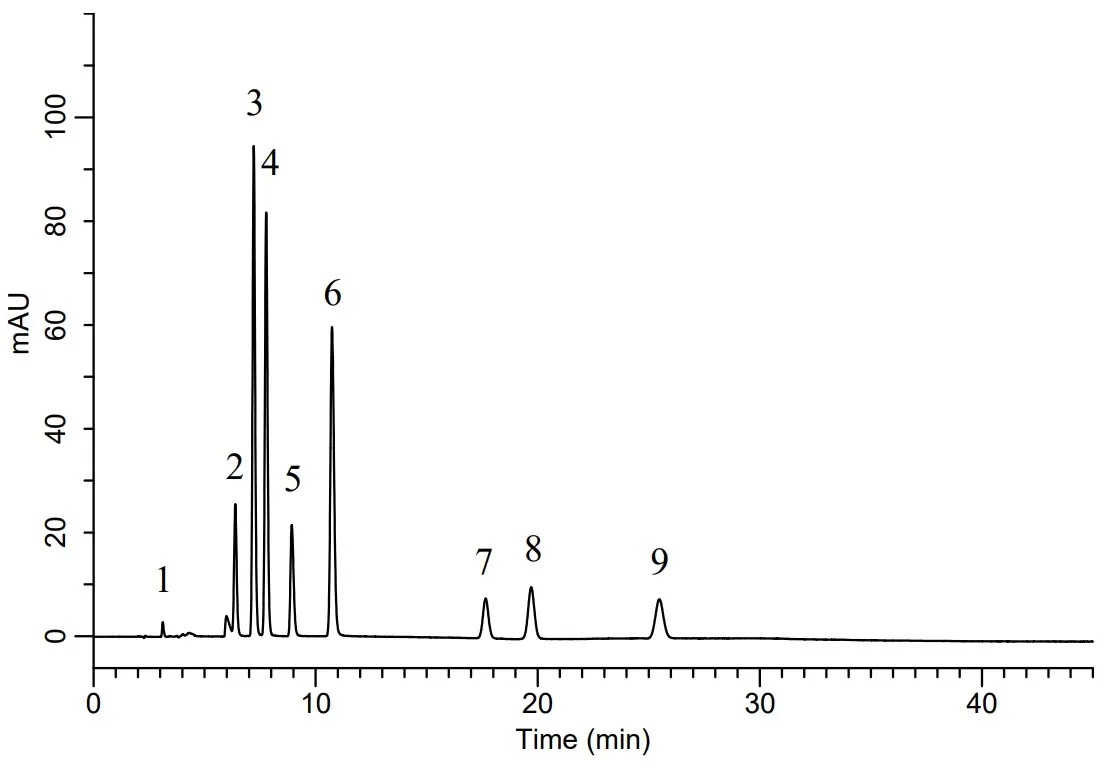
Peak identities
1. ascorbic acid 2. aspartame 3. caffeine 4. p-hydroxybenzoic acid 5. acesulfame potassium 6. saccharin sodium 7. sorbic acid 8. benzoic acid 9. dehydroacetic acid
Test conditions
Column: Inertsil Ph 250x4.6mm, 5µm (5020-01328)
Mobile phase A: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase B: 0.1% phosphoric acid in water
Isocratic: A/B 15%/85%
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Temperature: 40 °C
Detection: UV, 210 nm
Injection volume: 10 µL

HILIC LC/MS Analysis of various Stevia Glycosides with Shodex Asahipak NH2P40
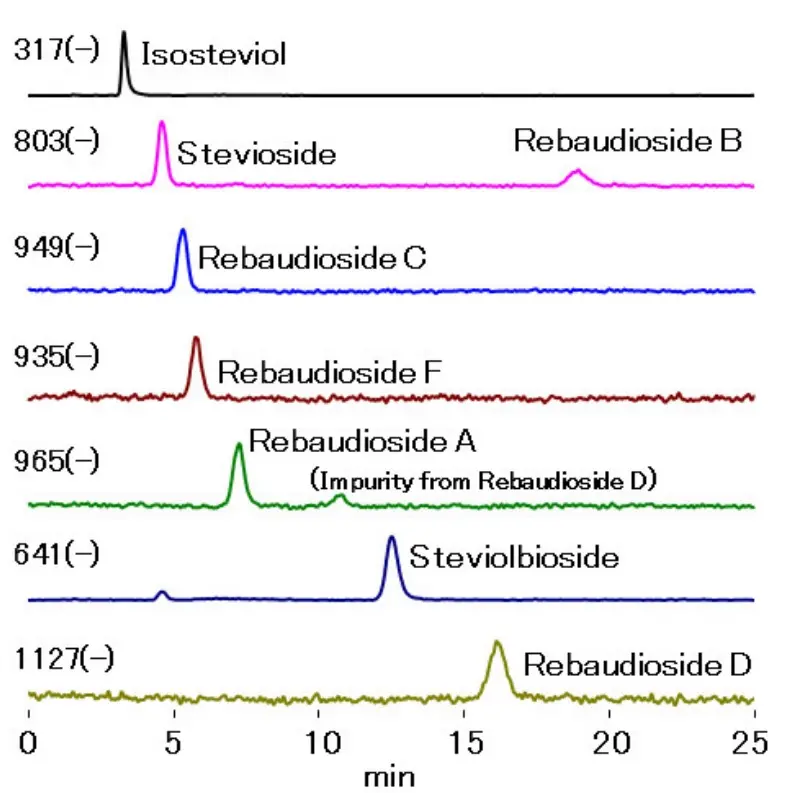
Peak identities
1. isosteviol 2. stevioside 3. rebaudioside C 4. rebaudioside F 5. rebaudioside A 6. steviol bioside 7. rebaudioside D
Test conditions
Column: Asahipak NH2P-40 2D 150x2.0mm
Mobile phase A: 0.1% NH3
Mobile phase B: Acetonitrile
Isocratic: 78%B
Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min
Detection: ESI-MS (SIM Negative)
Temperature: 30 °C

Downloads
Avantor ACE
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Avantor ACE Excel 1.7 C18, 1.7µm
- Avantor ACE Excel 2 Super C18, 2µm
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Avantor ACE 5 C18, 5µm
Chromanik
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- SunShell C18, 2.6µm
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- SunShell C18, 2µm
HPLC - HILIC:
- SunShell HILIC-Amide, 2.6µm
GL Sciences
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Inertsil Ph, 5µm
- Inertsil ODS-4, 5µm
- Inertsil NH2, 5µm
Imtakt
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Unison UK-C8, 3µm
Macherey-Nagel
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Nucleodur Phenyl Hexyl, 5µm
- Nucleodur C8 ec, 5µm
Nouryon - Kromasil
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Kromasil EternityXT C8, 2.5µm
Shodex
HPLC - HILIC:
- Asahipak NH2P-40 2D
Thermo Fisher
HPLC - Mixed-Mode:
- Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1, 5µm
Tosoh
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- TSKgel ODS-100V, 3µm
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.


![[English:] [English:]](https://cms.mz-at.de/fileadmin/_processed_/f/d/csm_logo_avantor-ace_web23_w600-h225px_7d5acb3b41.webp)
















