Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
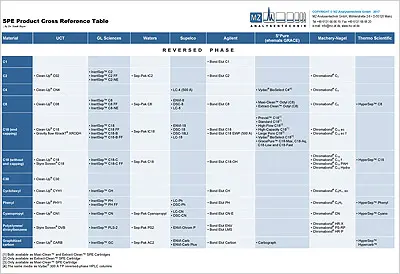
SPE Cartridges
Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)
SPE cartridges are an essential tool in solid phase extraction (SPE), which are used for the enrichment of analytes and the removal of interfering matrix components and accompanying substances . They consist of a housing filled with a sorbent to adsorb specific compounds from a sample. By using different sorbents, these cartridges can be customised to extract a variety of analytes from different matrices, making them a versatile tool in laboratories, especially in environmental analysis, bioanalysis and food control.
Our MZ-AT range includes many SPE cartridges from well-known manufacturers such as GL Sciences, United Chemical Technologies, S'Pure, Waters and Welch. We would be happy to provide you with customised offers of selected SPE cartridges suitable for your analysis. Simply contact us using the contact button!