- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Heparin
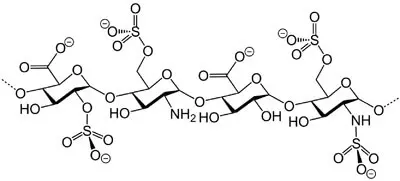
Heparin refers to a group of the body's own unbranched glucosaminoglycans (polysaccharides) that have an inhibitory effect on the blood coagulation cascade. The monomer units of these polysaccharides are glucosamine, glucuronic acid and iduronic acid. In many cases, they carry sulphate groups on the oxygen and nitrogen atoms of the side chains. The molecular weight of heparin is approximately between 4000 and 50000 g/mol. The figure opposite shows a structural section of a heparin molecule.
Due to the many functional groups present in the molecule, in particular the negatively charged sulphate or carboxylate groups, heparin is a very polar molecule which exhibits good solubility properties in water. Suitable separation techniques therefore include ion exchange chromatography and gel filtration chromatography (SEC with aqueous eluents). Below you will find some application examples.
Products
Applications
Size Exclusion Chromatography of Enoxaparin with Sepax Zenix SEC
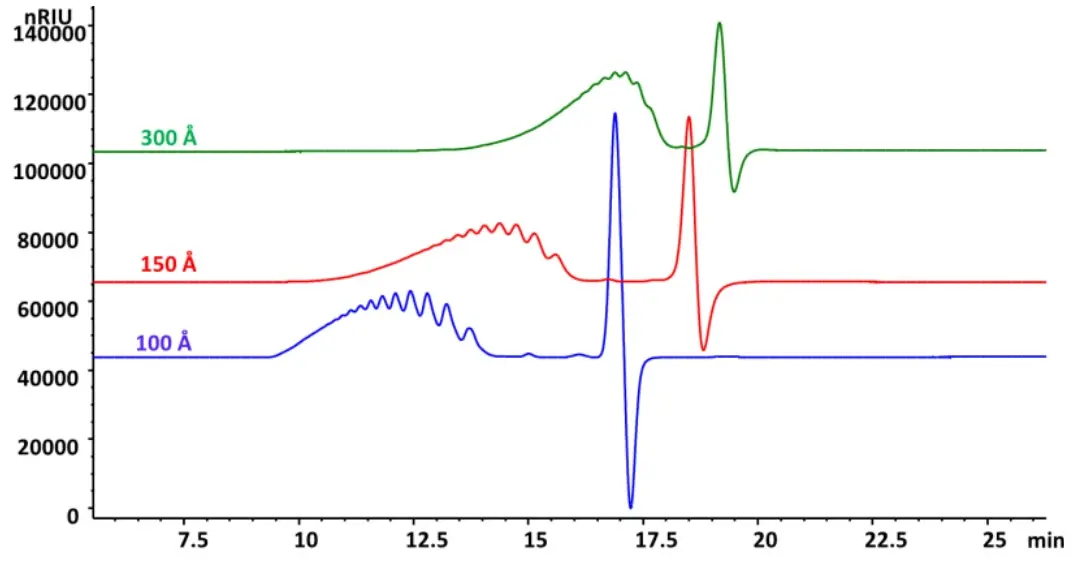
Peak identities
Enoxaparin Sodium
Test conditions
Column: Zenix SEC-100 300x7.8mm, 3µm
Zenix SEC-150 300x7.8mm, 3µm
Zenix SEC-300 300x7.8mm, 3µm
Mobile phase: 0.5 M LiNO3
Flow rate: 0.6 mL/min
Detection: RI (35 °C)
Temperature: 30 °C
Injection volume: 25 µL
Sample: 10 mg/mL enoxaparin sodium in mobile phase, MW 3,000 - 8,000 Da

Ion Exchange Chromatography of Heparin with Sepax Glycomix SAX
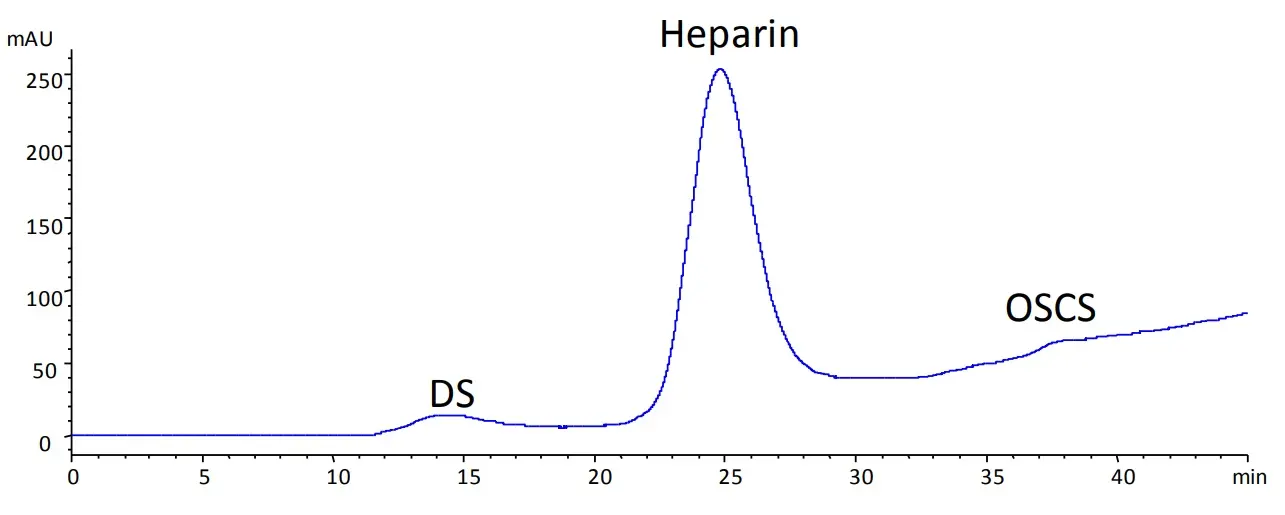
Peak identities
1. DS (Dermatan Sulfate) 2. heparin 3. OSCS (Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate)
Test conditions
Column: Glycomix SAX 250x4.6mm (901665-4625)
Mobile phase A: 0.04% NaH2PO4, pH 3
Mobile phase B: 0.04% NAH2PO4 + 14% NaClO4, pH 3
Gradient: 20 %B to 90 %B in 60 min
Flow rate: 0.22 mL/min
Temperature: 25 °C
Detection: UV, 202 nm
Injection volume: 10 µL

Downloads
Imtakt
UHPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Presto FF-C18, 2µm
Sepax
HPLC - SEC:
- SRT SEC-300, 5µm
- SRT SEC-500, 5µm
- Zenix SEC-100, 3µm
- Zenix SEC-150, 3µm
- Zenix SEC-300, 3µm
HPLC - IEX:
- Glycomix SAX
Shodex
HPLC - SEC:
- OHpak SB-804 HQ, 10µm
- OHpak SB-806M HQ, 13µm
- OHpak LB-806M, 13µm
Thermo Fisher
HPLC - Ion chromatography:
- Dionex IonPac AS11-HC, 4µm
- Dionex CarboPac PA20, 6.5µm
Tosoh
HPLC - SEC
- TSKgel G2000SWXL, 5µm
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.










