- 3% Discount on online orders
- Fast Delivery Times
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Manufacturer Expertise
- Contact Us
Checkout using your account
Checkout as a new customer
Creating an account has many benefits:
- See order and shipping status
- Track order history
- Check out faster
Antibodies mAb
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb's) are immunologically active proteins that have increasingly become the focus of medical research in recent years. Today, a large number of modern pharmaceuticals and therapeutic approaches based on monoclonal antibodies already exist
The analysis of monoclonal antibodies is usually aimed at separating monomers from dimers, trimers and other aggregates, as these can have a negative impact on the effectiveness of biopharmaceuticals. Furthermore, various fragments of mAb's can also be analysed, e.g. Fc or Fab fragments. The analysis of monoclonal antibodies can be carried out using different chromatographic separation techniques.
Products
Applications
1. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) with Tosoh TSkgel SuperSW mAb HR
SEC is a very suitable and widely used method for the determination of aggregate, monomer and fragment contents of mAb's in analyte solutions.
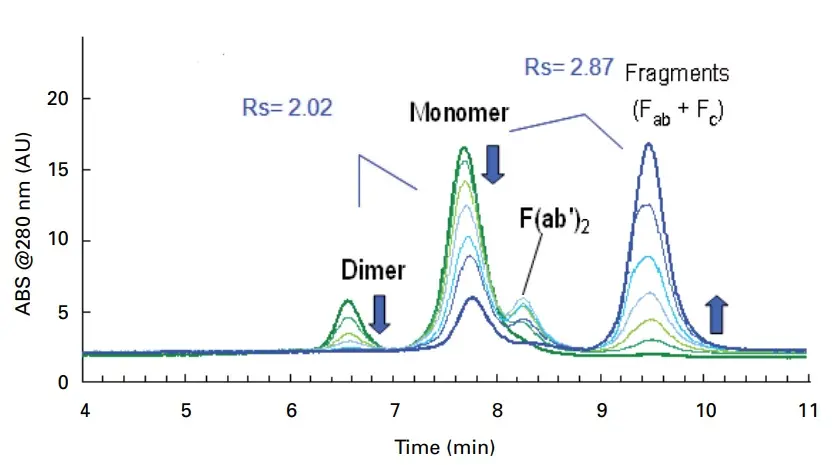
Peak identities
Dimer, monomer and fragments of IgG
Test conditions
Column: TSKgel SuperSW mAb HR 300x7.8mm
Mobile phase: 200 mmol/L phosphate buffer + 0.05% NaN3, pH 6.7
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Sample: 10 g/L IgG digested with papain for 0-24 h
Injection volume: 10 µL
Temperature: 25 °C
Detection: UV, 280 nm

2. Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) with Tosoh TSKgel Butyl-NPR
The separation in hydrophilic interaction chromatography is based on the different surface hydrophobicity of various proteins. If this is the case for the respective analytes, HIC can be used to separate different antibodies from each other, to separate antibodies from other proteins and also to separate antibody aggregates from monomers. The separation of antibody fragments is also possible.
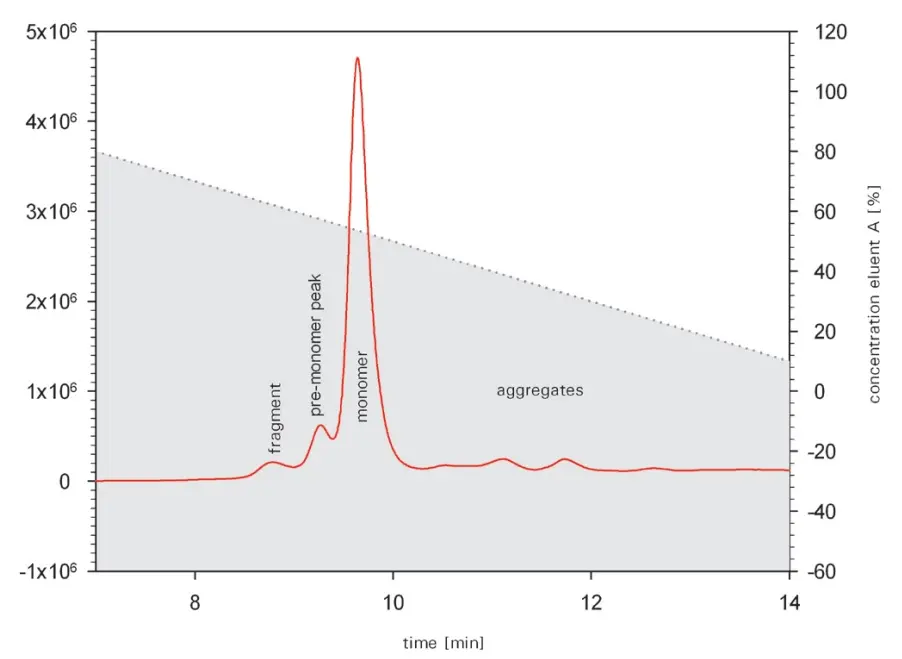
Peak identities
Fragments and aggregates of MAb
Test conditions
Column: TSKgel Butyl-NPR 35x4.6mm
Mobile phase A: Buffer with 3 M NaCl and 10 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7
Mobile phase B: 10 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7
Gradient: 0% - 100% B in 25min
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Detection: Fluorescence
Sample: 2 µg protein

3. Ion Exchange Chromatography with Tosoh TSKgel SP-STAT and CM-STAT
Ion exchange chromatography can be used to separate different charge variants of antibodies, fragments, aggregates and other proteins. The different charge variants result from the deamidation of asparagine or glutamine residues or from incomplete removal of the C-terminus of lysine residues.
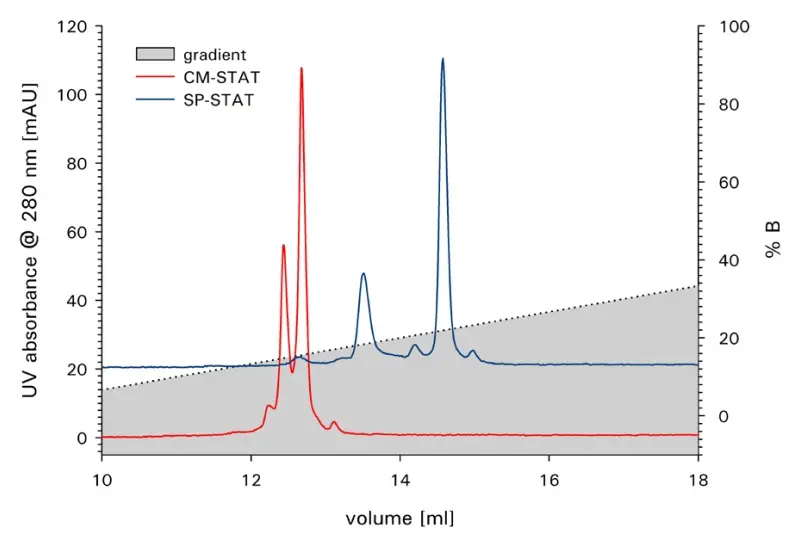
Peak identities
Separation of charge variants of an MAb
Test conditions
Columns: TSKgel SP-STAT 100x4.6mm, 7µm
TSKgel CM-STAT 100x4.6mm, 7µm
Mobile phase A: 10 mM/L sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7
Mobile phase B: 100mM/L sodium acetate buffer, pH 7
Gradient: 0% - 100% B in 30 min
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
Detection: UV, 280 nm
Sample: MAb 2 g/L

4. Reversed-Phase Chromatography with AMT HALO 1000Å C4
Reversed-phase chromatography can also be used to analyse different monoclonal antibodies.
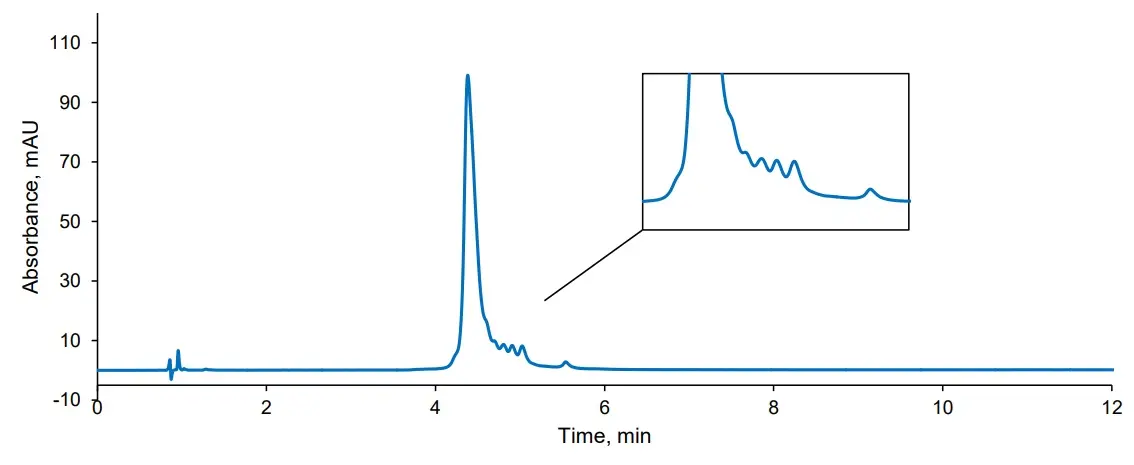
Test conditions
Column: HALO 1000Å C4 100x2.1mm, 2.7µm
Mobile phase A: water, 0.1% TFA
Mobile phase B: 80/20 acetonitrile/water, 0.085% TFA
Gradient: 40% - 47.5% B in 12 min
Flow rate: 0.4 mL/min
Pressure: 210 bar
Temperature: 80 °C
Injection volume: 2 µL
Sample solvent: 70/30 water/acetonitrile
Detection: UV, 280 nm

Downloads
Sepax™ Technologies
HPLC - SEC:
- SRT-10, SRT-10C
- SRT, SRT-C
- Zenix, Zenix-C
- Unix, Unix-C
HPLC - HIC:
- Proteomix HIC Ethyl
- Proteomix HIC Propyl
- Proteomix HIC Butyl
- Proteomix HIC Phenyl
HPLC - IEX:
- Antibodix-NP1.7, -NP3, -NP5 und -NP10
- Proteomix SCX-NP1.7, -NP3, NP5 und -NP10
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- Proteomix RP-300
- Proteomix RP-500
- Proteomix RP-1000
- Sepax Zenix SEC-300 Zenix-C SEC-300 SEC Screening Kit
- Sepax SRT-C 300 Analysis of MAb SEC
- Sepax Unix-C SEC-300 MAb Separation
- MAb Purification on SRT-10 300
- Sepax Zenix-C SEC-300 Rituximab Analysis
- Sepax SRT-300 Separation of Monoclonal Antibody
- Sepax Antibodix NP10 Analysis of MAb with Charge Variance
- Sepax Antibodix NP10 Analysis of MAb-X22 Impact of Initial Salt
- Sepax Antibodix NP10 Analysis of MAb-X22 Impact of Mobile Phase Ph
- Sepax Antibodix WCX-NP3 Analysis of MAb
- Sepax Proteomix SCX-NP5 MAb-IgG1 & IgG2 Charge Variants Separation
- Sepax Antibodix WCX-NP5 Proteomix SCX-NP5 Ion Exchange Kit for MAb-separation
- Sepax Proteomix HIC-Butyl-1.7 Intact & Oxidized MAb Analysis
- Sepax Proteomix HIC-Butyl-NP5 Erbitux & Rituximab MAb Separation
- Sepax Proteomix RP-1000 Column Temperature-Effect-on-MAb Separation
- Sepax Proteomix RP-1000 Proteomix RP-500 MAb Fragment
Shodex™
HPLC - SEC:
- PROTEIN LW-803
Tosoh Bioscience™
HPLC - SEC:
- TSKgel G3000SWXL
- TSKgel UP-SW3000
- TSKgel SuperSW mAb HR
- TSKgel SuperSW mAb HTP
- TSKgel UltraSW Aggregate
HPLC - HIC:
- TSKgel Phenyl-5PW
- TSKgel Ether-5PW
- TSKgel Butyl-NPR
HPLC - IEX:
- TSKgel SP-STAT
- TSKgel CM-STAT
- TSKgel Q-STAT und DNA-STAT
HPLC - Reversed Phase:
- TSKgel Protein C4-300
- Tosoh TSKgel G3000SWXL TSKgel SuperSW mAb HR TSKgel SuperSW mAb HTP High Speed and Resolution SEC Analysis of mAbs Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel UP-SW3000 UHPLC Analysis of Immunoglobulins Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel UP-SW3000 Inceased Monoclonal Antibody Resolution Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Protein A-5PW Reproducible and Robust Antibody Titer Analysis Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Butyl-NPR TSKgel G3000SWXL mAb Aggregate Detection Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel SP-STAT TSKgel CM-STAT Fast Analysis of IgG Charge Heterogeneity Applications
- Tosoh TSKgel Q-STAT TSKgel DNA-STAT Brochure
- Tosoh TSK-GEL SP-STAT and CM-STAT Columns
- Waters BioResolve RP mAb Improving the Recovery of Intact Antibodies
- Waters BioResolve RP mAb Polyphenyl Direct LC-MS Characterization of Glycoform Distribution and Low Molecular Weight Impurities in mAb
- Waters BioResolve RP mAb Polyphenyl Protein Quantification in Formulation Buffer
- Waters BioResolve RP mAb Polyphenyl Triple Quadrupole MS for the Quantification of mAb Light Chains in Plasma
- Waters BioResolve SCX mAb Development of mAb Charge Variant Analysis Methods
- Waters BioResolve SCX mAb Online IEX-MS of mAb Charge Variants
- Waters BioResolve SCX mAb Optimizing LC-MS Separations of mAbs
- Waters BioResolve SCX mAb Development of pH Gradient Mobile Phase Concentrates for Robust, High Resolution mAb Charge Variant Analysis
- Waters BioResolve SCX mAb Designing a New Particle Technology for Robust Charge Variant Analysis of mAbs
- Waters BioResolve SEC mAb High Resolution SEC Separations of mAb Aggregates, Monomers and Fragments
- Waters BioResolve SEC mAb Guard Columns for Production Process and Formulation Development Samples
- Waters BioResolve SEC mAb Modern SEC Separations of Biosimilar Antibodies at Physiological pH and Ionic Strength
The right column for you - we will be happy to support you individually
Competent consultants are always at your side. Write a message to our consultants, we will get back to you and give you individual support.









