- 3% Nachlass bei Online-Bestellung
- Schnelle Lieferzeiten
- DIN ISO 9001:2015 zertifiziert
- Herstellerexpertise
- Kontaktieren Sie uns
Auschecken über Ihr Konto
Als Neukunde auschecken
Ein Konto zu erstellen hat viele Vorteile:
- Bestellungen und Sendungen verfolgen
- Alte Bestellungen einsehen
- Schneller zur Kasse gehen
Ionenaustauschchromatographie
Die Ionenaustauschchromatographie (IEX) dient der Trennung und Analyse von geladenen bzw. ionisierbaren Molekülen. Es wird zwischen Anionen- und Kationenaustauscher unterschieden, des Weiteren zwischen starken und schwachen Austauschern.
- SAX: starker Anionaustauscher (Strong Anion Exchanger)
- WAX: schwacher Anionaustauscher (Weak Anion Exchanger)
- SCX: starker Kationaustauscher (Strong Cation Exchanger)
WCX: schwacher Kationaustauscher (Weak Cation Exchanger)
Die Ionenaustauschchromatographie wird häufig als Biotrenntechnik für Proteine und Antikörper verwendet. Proteine werden dabei nach ihrer Netto- oder Oberflächenladung getrennt, die abhängig ist von dem pH-Wert und der Ionenstärke der mobilen Phase. Weitere Anwendungsgebiete sind Oligonucleotide, Zucker, RNA- und DNA-Moleküle und weiteres mehr.
Die Ionenchromatographie und die Ionenausschlusschromatographie sind zwei Spezialfälle der Ionenaustauschchromatographie mit eigenen Säulentechnologien für spezifische Anwendungen.
Produkte
Technische Daten
Eine Elutionsreihenfolge ist für die Ionenaustauschchromatographie (IEX) oft schwer vorhersagbar, weil die Elution bzw. Retention von Molekülen von vielen Parametern abhängig ist. Wichtige Größen sind dabei unter Anderem der Typ des verwendeten Ionentauschers, der pH-Wert, die Ionenstärke und die Art des Gegenions der mobilen Phase, sowie die elektronischen Eigenschaften der Analyten.
Die Oberfläche der stationären Phasen tragen ionische Gruppen, die nach außen hin durch bewegliche Gegenionen der mobilen Phase neutralisiert werden.

Die Analytmoleküle konkurrieren untereinander und mit den vorhandenen Gegenionen der mobilen Phase um einen Platz an der Oberfläche der stationären Phase. Stärker geladene Analytmoleküle werden in der Regel auch stärker retadiert als solche, die nur schwache Ladungen aufweisen oder neutral sind.

Anionenaustauscher tragen auf der Oberfläche positive Ladungen, z. B. quarternäre oder primäre Ammoniumgruppen, um Anionen zu binden. Kationenaustauscher tragen demnach negative Ladungen an der Oberfläche,
z. B. Sulfonate oder Carboxylate, um Kationen zu binden (Beispiele siehe Abbildung).
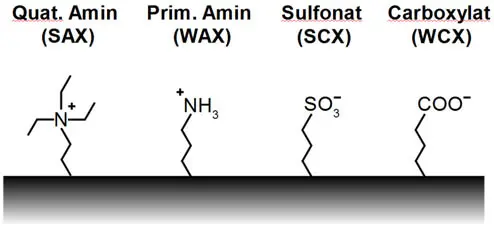
Wie wähle ich die richtige Ionenaustausch-Säule aus?
Die Auswahl einer passenden Ionenaustausch-Säule ist sehr komplex und von vielen Paramatern abhängig, wie z.B. vom pH-Wert, die Ionenstärke und den elektronischen Eigenschaften der Analyten.
Zunächst ist es jedoch entscheidend, welche Art von Ionen untersucht werden sollen (Anionen oder Kationen). Dementsprechend gibt es starke und schwache Austauscher Säulen. Starke Ionenaustausch-Säulen besitzen eine Ladung unabhängig vom eingesetzten pH-Wert. Dadurch bleibt die Retention auch bei einer pH-Wert Änderung stabil (abhängig vom Analyten). Bei schwachen Austauscher-Säulen ändert der pH-Wert die Ionisierung der stationären Phase und dadurch die Eigenschaften. Die Retention kann folglich über den pH-Wert gesteuert werden.
Da die Elution auf Grund der Vielzahl an unterschiedlichen Parametern schwer vorhersehbar ist, empfiehlt sich vor der Wahl der Säule eine Recherche in der Literatur oder bei verschiedenen Herstellern. Wir helfen Ihnen gerne bei der Auswahl der passenden Säule. Kontaktieren Sie uns!
Hersteller und Säulen der Ionenaustauschchromatographie
1. Säulen für die Kationaustauschchromatographie
| Hersteller | Name | Basismaterial | Modifizierung | Porengröße | Partikelgröße | pH-Bereich |
| Tosoh Bioscience | TSKgel CM-2SW | Silica gel | Carboxymethyl (Na+) | 125 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
TSKgel CM-3SW | Silica gel | Carboxymethyl (Na+) | 250 Å | 10 µm | 2.0–7.5 | |
TSKgel SP-2SW | Silica gel | Sulfopropyl (Na+) | 125 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–7.5 | |
TSKgel CM-5PW | Polymethacrylate | Carboxymethyl (Na+) | 1000 Å | 10 & 13 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel SP-5PW | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl (Na+) | 1000 Å | 10, 13 & 20 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel SP-NPR | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl (Na+) | non-porous | 2.5 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel SP-STAT | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl (Na+) | non-porous | 7 & 10 µm | 3.0–10.0 | |
TSKgel CM-STAT | Polymethacrylate | Carboxymethyl (Na+) | non-porous | 7 & 10 µm | 3.0–10.0 | |
TSKgel Bioassist S PEEK | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl (Na+) | ~1300 Å | 7 & 13 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel SCX (Na+) | PS/DVB | Sulfonic acid (Na+) | 60 Å | 5 µm | 1.0–14.0 | |
TSKgel SCX (H+) | PS/DVB | Sulfonic acid (H+) | 60 Å | 5 µm | 1.0–14.0 | |
| Shodex | IEC SP-825 | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl | 5000 Å | 8 µm | 2.0–12.0 |
IEC SP-2025 | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl | 5000 Å | 20 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
IEC SP-FT 4A | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl | non-porous | 2.7 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
IEC CM-825 | Polymethacrylate | Carboxymethyl | 5000 Å | 8 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
IEC CM-2025 | Polymethacrylate | Carboxymethyl | 5000 Å | 20 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
Asahipak ES-502C 7C | Polymethacrylate | Carboxymethyl | 2000 Å | 9 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
Asahipak ES-502C 20C | Polymethacrylate | Carboxymethyl | 2000 Å | 13 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
CXpak P-421S | PS/DVB | Sulfonic acid (Na+) | N/A | 6 µm | 3.0–14.0 | |
CXpak P-G | PS/DVB | Sulfonic acid (Na+) | N/A | 6 µm | 3.0–14.0 | |
| Sepax | Proteomix SCX | PS/DVB with neutral | Sulfonate | non-porous | 1.7, 3, 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 |
Proteomix WCX | PS/DVB with neutral | Carboxylate | non-porous | 1.7, 3, 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
Antibodix WCX | PS/DVB with neutral | Carboxylate | non-porous | 1.7, 3, 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
| GL Sciences | InertSil CX | Silica Gel | Benzenesulfonic acid | 100 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
| Macherey-Nagel | Nucleogel SCX | Polymethacrylate | Sulfonate | 1000 Å | 8 µm | 1.0–13.0 |
| Separation Methods Technologies | SMT SCX | Silica Gel | Sulfonic acid | 100 Å, 300 Å | 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
SMT WCX | Silica Gel | Carboxylic acid | 100 Å, 300 Å | 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–7.5 | |
| Supelco | Discovery Bio PolyMA-SCX | Polymethacrylate | Sulfopropyl (Na+) | 1000 Å | 5 µm | 1.0–13.0 |
| Thermo Scientific | BioBasic SCX | Silica Gel | Sulfonic acid | 300 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
ProPac SCX-10 | Ethylvinylbenzene crosslinked | Sulfonic acid | non-porous | 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProPac SCX-20 | Ethylvinylbenzene crosslinked | Sulfonic acid | non-porous | 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProPac WCX-10 | Ethylvinylbenzene crosslinked | Carboxylic acid | non-porous | 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProPac Elite WCX | DVB particles with | Carboxylic acid | non-porous | 5 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProSwift SCX-1S | Polymethacrylate | Sulfonic acid | N/A | monolithic | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProSwift WCX-1S | Polymethacrylate | Carboxylic acid | N/A | monolithic | 2.0–12.0 | |
MAbPac SCX-10 | Polydivinylbenzene | Sulfonic acid | non-porous | 3, 5, & 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 |
2. Säulen für die Anionaustauschchromatographie
| Hersteller | Name | Basismaterial | Modifizierung | Porengröße | Partikelgröße | pH-Bereich |
| Tosoh Bioscience | TSKgel BioAssist Q | Polymethacrylate | Polyamine (Cl−) | ~4000 Å | 10 & 13 µm | 2.0–12.0 |
TSKgel SuperQ-5PW | Polymethacrylate | Trimethyl-amino (Cl−) | 1000 Å | 10 & 13 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel DEAE-5PW | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl (Cl−) | 1000 Å | 10, 13 & 20 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel Q-STAT | Polymethacrylate | Trimethyl-amino (Cl−) | non-porous | 7 & 10 µm | 3.0–10.0 | |
TSKgel DNA-STAT | Polymethacrylate | Trimethyl-amino (Cl−) | non-porous | 5 µm | 3.0–10.0 | |
TSKgel DEAE-NPR | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl (Cl−) | non-porous | 2.5 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel DNA-NPR | Polymethacrylate | Proprietary (ClO4−) | non-porous | 2.5 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
TSKgel DEAE-2SW | Silica Gel | Diethylaminoethyl (H2PO4−) | 125 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–7.5 | |
TSKgel DEAE-3SW | Silica Gel | Diethylaminoethyl (Cl−) | 250 Å | 10 µm | 2.0–7.5 | |
TSKgel SUGAR AXI | PS/DVB | Trimethyl-amino (HBO3−) | 60 Å | 8 µm | 1.0–14.0 | |
TSKgel SUGAR AXG | PS/DVB | Trimethyl-amino (HBO3−) | 60 Å | 10 µm | 1.0–14.0 | |
TSKgel SAX | PS/DVB | Trimethyl-amino (Cl−) | 60 Å | 5 µm | 1.0–14.0 | |
| Shodex | IEC QA-825 | Polymethacrylate | Quat. Ammonium | 5000 Å | 12 µm | 2.0–12.0 |
IEC QA-2025 | Polymethacrylate | Quat. Ammonium | 5000 Å | 20 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
IEC DEAE-825 | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl | 5000 Å | 8 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
IEC DEAE-2025 | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl | 5000 Å | 20 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
AXpak WA-624 | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl | 2000 Å | 10 µm | 3.0–12.0 | |
Asahipak ES-502N 7C | Polyvinylalcohol | Diethylaminoethyl | 2000 Å | 9 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
Asahipak ES-502N 20C | Polyvinylalcohol | Diethylaminoethyl | 2000 Å | 13 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
| Sepax | Proteomix SAX | PS/DVB with neutral | Quat. Ammonium | non-porous | 1.7, 3, 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 |
Proteomix WAX | PS/DVB with neutral | Diethylaminoethyl | non-porous | 1.7, 3, 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
Glycomix SAX | Hydrophilic polymer | Quat. Ammonium | N/A | N/A | 2.0–12.0 | |
| GL Sciences | InertSil AX | Silica Gel | Diethylaminopropyl | 100 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
| Macherey-Nagel | Nucleogen DEAE | Silica Gel | Diethylaminoethyl | 60, 500, 4000 Å | 7 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
Nucleogel SAX | Quaternisiertes PEI | Quat. Ammonium | 1000 Å | 8 µm | 1.0–13.0 | |
| Separation Methods Technologies | SMT SAX | Silica Gel | Quat. Ammonium | 100, 300 Å | 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–7.5 |
SMT WAX | Silica Gel | Polyethyleneimine | 100, 300 Å | 5 & 10 µm | 2.0–7.5 | |
| Supelco | Discovery Bio PolyMA-WAX | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl | 1000 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–11.0 |
| Thermo Scientific | Hypersil Gold AX | Silica Gel | Polyethyleneimine | 175 Å | 1.9, 3 & 5 µm | 2.0–8.0 |
HyperSil Gold SAX | Silica Gel | Quat. Ammonium | 175 Å | 1.9, 3 & 5 µm | 2.0–8.0 | |
BioBasic AX | Silica Gel | Polyethyleneimine | 300 Å | 5 µm | 2.0–8.0 | |
ProPac SAX-10 | Ethylvinylbenzene crosslinked | Quat. Ammonium | non-porous | 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProPac WAX-10 | Ethylvinylbenzene crosslinked | Tertiary Amine | non-porous | 10 µm | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProSwift SAX-1S | Polymethacrylate | Quat. Ammonium | N/A | monolithic | 2.0–12.0 | |
ProSwift WAX-1S | Polymethacrylate | Diethylaminoethyl | N/A | monolithic | 2.0–12.0 | |
DNAPac PA100 | Pellicular polymer beads | Quat. Ammonium | non-porous | 13 µm | 2.0–12.5 | |
DNAPac PA200 | Pellicular polymer beads | Quat. Ammonium | non-porous | 8 µm | 2.0–12.5 | |
DNAPac PA200RS | Pellicular polymer beads | Quat. Ammonium | non-porous | 4 µm | 2.0–12.5 | |
DNASwift SAX-1S | Polymethacrylate | Quat. Ammonium | N/A | monolithic | 6.0–12.4 |
Die passende Säule für Sie - Gerne beraten wir Sie persönlich
Unsere Experten stehen Ihnen jederzeit zur Seite. Schreiben Sie unserem Team eine Nachricht. Wir melden uns zurück und beraten Sie ganz individuell.
Sie finden bei uns:
Schreiben Sie uns eine Nachricht und wir werden uns schnellstmöglich bei Ihnen melden.
